Home > Press > Electric fields remove nanoparticles from blood with ease
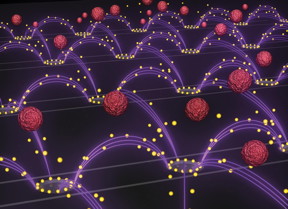 |
| An artist's representation of the nanoparticle removal chip developed by researchers in Professor Michael Heller's lab at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. An oscillating electric field (purple arcs) separates drug-delivery nanoparticles (yellow spheres) from blood (red spheres) and pulls them towards rings surrounding the chip's electrodes. The image is featured as the inside cover of the Oct. 14 issue of the journal Small. CREDIT: Stuart Ibsen and Steven Ibsen. |
Abstract:
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego developed a new technology that uses an oscillating electric field to easily and quickly isolate drug-delivery nanoparticles from blood. The technology could serve as a general tool to separate and recover nanoparticles from other complex fluids for medical, environmental, and industrial applications.
Electric fields remove nanoparticles from blood with ease
San Diego, CA | Posted on November 24th, 2015Nanoparticles, which are generally one thousand times smaller than the width of a human hair, are difficult to separate from plasma, the liquid component of blood, due to their small size and low density. Traditional methods to remove nanoparticles from plasma samples typically involve diluting the plasma, adding a high concentration sugar solution to the plasma and spinning it in a centrifuge, or attaching a targeting agent to the surface of the nanoparticles. These methods either alter the normal behavior of the nanoparticles or cannot be applied to some of the most common nanoparticle types.
"This is the first example of isolating a wide range of nanoparticles out of plasma with a minimum amount of manipulation," said Stuart Ibsen, a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of NanoEngineering at UC San Diego and first author of the study published October in the journal Small. "We've designed a very versatile technique that can be used to recover nanoparticles in a lot of different processes."
This new nanoparticle separation technology will enable researchers -- particularly those who design and study drug-delivery nanoparticles for disease therapies -- to better monitor what happens to nanoparticles circulating in a patient's bloodstream. One of the questions that researchers face is how blood proteins bind to the surfaces of drug-delivery nanoparticles and make them less effective. Researchers could also use this technology in the clinic to determine if the blood chemistry of a particular patient is compatible with the surfaces of certain drug-delivery nanoparticles.
"We were interested in a fast and easy way to take these nanoparticles out of plasma so we could find out what's going on at their surfaces and redesign them to work more effectively in blood," said Michael Heller, a nanoengineering professor at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering and senior author of the study.
The device used to isolate the drug-delivery nanoparticles was a dime-sized electric chip manufactured by La Jolla-based Biological Dynamics, which licensed the original technology from UC San Diego. The chip contains hundreds of tiny electrodes that generate a rapidly oscillating electric field that selectively pulls the nanoparticles out of a plasma sample. Researchers inserted a drop of plasma spiked with nanoparticles into the electric chip and demonstrated nanoparticle recovery within 7 minutes. The technology worked on different types of drug-delivery nanoparticles that are typically studied in various labs.
The breakthrough in the technology relies on designing a chip that can work in the high salt concentration of blood plasma. The chip's ability to pull the nanoparticles out of plasma is based on differences in the material properties between the nanoparticles and plasma components. When the chip's electrodes apply an oscillating electric field, the positive and negative charges inside the nanoparticles reorient themselves at a different speed than the charges in the surrounding plasma. This momentary imbalance in the charges creates an attractive force between the nanoparticles and the electrodes. As the electric field oscillates, the nanoparticles are continually pulled towards the electrodes, leaving the rest of the plasma behind. Also, the electric field is designed to oscillate at just the right frequency: 15,000 times per second.
"It's amazing that this method works without any modifications to the plasma samples or to the nanoparticles," said Ibsen.
###
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Cancer
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








