Home > Press > These microscopic fish are 3-D-printed to do more than swim: Researchers demonstrate a novel method to build microscopic robots with complex shapes and functionalities
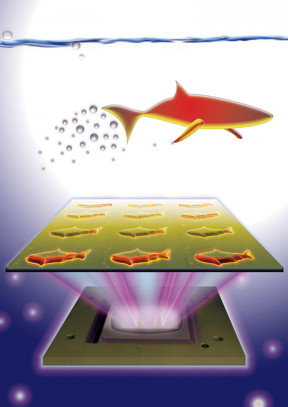 |
| 3-D-printed microfish contain functional nanoparticles that enable them to be self-propelled, chemically powered and magnetically steered. The microfish are also capable of removing and sensing toxins. CREDIT: J. Warner, UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. |
Abstract:
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego used an innovative 3D printing technology they developed to manufacture multipurpose fish-shaped microrobots -- called microfish -- that swim around efficiently in liquids, are chemically powered by hydrogen peroxide and magnetically controlled. These proof-of-concept synthetic microfish will inspire a new generation of "smart" microrobots that have diverse capabilities such as detoxification, sensing and directed drug delivery, researchers said.
These microscopic fish are 3-D-printed to do more than swim: Researchers demonstrate a novel method to build microscopic robots with complex shapes and functionalities
San Diego, CA | Posted on August 26th, 2015The technique used to fabricate the microfish provides numerous improvements over other methods traditionally employed to create microrobots with various locomotion mechanisms, such as microjet engines, microdrillers and microrockets. Most of these microrobots are incapable of performing more sophisticated tasks because they feature simple designs -- such as spherical or cylindrical structures -- and are made of homogeneous inorganic materials. In this new study, researchers demonstrated a simple way to create more complex microrobots.
The research, led by Professors Shaochen Chen and Joseph Wang of the NanoEngineering Department at the UC San Diego, was published in the Aug. 12 issue of the journal Advanced Materials.
By combining Chen's 3D printing technology with Wang's expertise in microrobots, the team was able to custom-build microfish that can do more than simply swim around when placed in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide. Nanoengineers were able to easily add functional nanoparticles into certain parts of the microfish bodies. They installed platinum nanoparticles in the tails, which react with hydrogen peroxide to propel the microfish forward, and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the heads, which allowed them to be steered with magnets.
"We have developed an entirely new method to engineer nature-inspired microscopic swimmers that have complex geometric structures and are smaller than the width of a human hair. With this method, we can easily integrate different functions inside these tiny robotic swimmers for a broad spectrum of applications," said the co-first author Wei Zhu, a nanoengineering Ph.D. student in Chen's research group at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego.
As a proof-of-concept demonstration, the researchers incorporated toxin-neutralizing nanoparticles throughout the bodies of the microfish. Specifically, the researchers mixed in polydiacetylene (PDA) nanoparticles, which capture harmful pore-forming toxins such as the ones found in bee venom. The researchers noted that the powerful swimming of the microfish in solution greatly enhanced their ability to clean up toxins. When the PDA nanoparticles bind with toxin molecules, they become fluorescent and emit red-colored light. The team was able to monitor the detoxification ability of the microfish by the intensity of their red glow.
"The neat thing about this experiment is that it shows how the microfish can doubly serve as detoxification systems and as toxin sensors," said Zhu.
"Another exciting possibility we could explore is to encapsulate medicines inside the microfish and use them for directed drug delivery," said Jinxing Li, the other co-first author of the study and a nanoengineering Ph.D. student in Wang's research group.
How this new 3D printing technology works
The new microfish fabrication method is based on a rapid, high-resolution 3D printing technology called microscale continuous optical printing (μCOP), which was developed in Chen's lab. Some of the benefits of the μCOP technology are speed, scalability, precision and flexibility. Within seconds, the researchers can print an array containing hundreds of microfish, each measuring 120 microns long and 30 microns thick. This process also does not require the use of harsh chemicals. Because the μCOP technology is digitized, the researchers could easily experiment with different designs for their microfish, including shark and manta ray shapes.
"With our 3D printing technology, we are not limited to just fish shapes. We can rapidly build microrobots inspired by other biological organisms such as birds," said Zhu.
The key component of the μCOP technology is a digital micromirror array device (DMD) chip, which contains approximately two million micromirrors. Each micromirror is individually controlled to project UV light in the desired pattern (in this case, a fish shape) onto a photosensitive material, which solidifies upon exposure to UV light. The microfish are built using a photosensitive material and are constructed one layer at a time, allowing each set of functional nanoparticles to be "printed" into specific parts of the fish bodies.
"This method has made it easier for us to test different designs for these microrobots and to test different nanoparticles to insert new functional elements into these tiny structures. It's my personal hope to further this research to eventually develop surgical microrobots that operate safer and with more precision," said Li.
###
This project was supported by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency-Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense (grants no. HDTRA1-14-1-0064 and HDTRA1-13-1-002), the National Science Foundation (grants no. CMMI-1120795 and CMMI-1332681) and National Institutes of Health (grants no. EB012597 and EB017876).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Robotics
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
![]() Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
Liquid metal sticks to surfaces without a binding agent June 9th, 2023
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








