Home > Press > Buckle up for fast ionic conduction
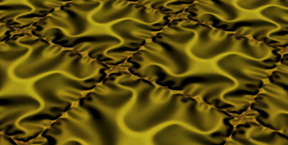 |
| ETH researchers engineered free-standing ceramic membranes for so-called micro energy converters. The strain patterns of these membranes control their properties. Illustration: Shi Y et al. Nature Materials 2015 |
Abstract:
ETH material engineers found that the performance of ion-conducting ceramic membranes that are so important in industry depends largely on their strain and buckling profiles. For the first time, scientists can now selectively manipulate the buckling profile, and thus the physical properties, allowing new technical applications of these membranes.
Buckle up for fast ionic conduction
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on June 16th, 2015"Ionics, ion-based data processing and energy conversion, is the electronics of the future", says Jennifer Rupp, a professor of Electrochemical Materials at ETH Zurich, and therewith sums up her field of research. Together with her group, Rupp produces ceramic materials that can conduct charged atoms (ions), such as oxygen or lithium ions, very quickly. Such materials are already being used today; for example, in lambda sensors of automotive catalytic converters and solid oxide fuel cells. The ETH professor is convinced that the industrial importance of these materials will even further increase - for example, in gas sensors, new classes of data storage and computer circuits, and in the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa.
One of the most important research questions in Rupp's field currently is how to optimise these materials, which are usually produced in the form of a thin membrane, so that ions can move more quickly within them. In a study just published in the scientific journal Nature Materials, several doctoral students in her group demonstrated how ion transport depends greatly on the manner in which these membranes are strained. The group also succeeded in controlling the strain of the membranes selectively, which is a breakthrough in the development of future technical applications.
Free-standing membrane
The scientists worked in their study with a very thin ceramic layer; namely, gadolinium-doped ceria. "This is one of the most frequently used ion conductors in the industry," explains Sebastian Schweiger, a doctoral student.
In previous research, the material had been usually studied in the form of a thin film on a silicon substrate. Yanuo Shi, another doctoral student in Rupp's group and first author of the recently published paper, instead created a free-standing membrane from the material by free-etching the substrate under the thin ceramic layer. The material was then no longer flat but buckled due to changes of the internal stress in the layer during the etching process. Shi attached microelectrodes to small pieces of these membranes to create tiny components that can be used to generate electricity from hydrogen or organic compounds and from oxygen in the air.
Electrode design affects buckling profile
The researchers also found that the arrangement of the electrodes affects the buckling profile of the ceramic membrane and the material structure at the atomic level. In turn, this greatly influences the conductivity of the membrane for oxygen ions. The scientists are able to describe this effect in detail. "For the first time, we are able to selectively control the buckling profile and ion conductivity of such membranes," says Alexander Bork, another doctoral student.
In recent decades, scientists have attempted mainly to influence the conductivity of such ion conductors by deliberately 'contaminating' the material with certain foreign atoms - in technical terms, doping. The ETH researchers have now shown that the conductivity can be controlled to a much greater degree by manipulation of the strain and buckling profile in real devices.
"Even in earlier experiments, scientists noticed that power generation in micro solid oxide fuel cells varies greatly depending on the structure of such cells. In the experiment with the strain of the ion conductor, we have now found a possible explanation for this behaviour," says Rupp. It now appears possible to optimise the characteristics of ion-conducting membranes. This supports the development of future gas sensors, ion-based data storage and micro energy converters, such as fuel cells - and potentially a range of other as yet unknown applications in the promising field of ionics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jennifer Rupp
41-792-900-697
Copyright © ETH Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Industrial
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Fuel Cells
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








