Home > Press > New composite material as CO2 sensor
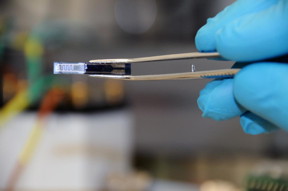 |
| ETH researchers' miniature CO2 sensor is pictured: chip with a thin layer of the polymer-nanoparticle composite. CREDIT: Fabio Bergamin / ETH Zurich |
Abstract:
Material scientists at ETH Zurich and the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam have developed a new type of sensor that can measure carbon dioxide (CO2). Compared with existing sensors, it is much smaller, has a simpler construction, requires considerably less energy and has an entirely different functional principle. The new sensor consists of a recently developed composite material that interacts with CO2 molecules and changes its conductivity depending on the concentration of CO2 in the environment. ETH scientists have created a sensor chip with this material that enables them to determine CO2 concentration with a simple measurement of electrical resistance.
New composite material as CO2 sensor
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on June 8th, 2015The basis of the composite material is a chain-like macromolecule (polymer) made up of salts called ionic liquids, which are liquid and conductive at room temperature. The name of the polymers is slightly misleading as they are called «poly(ionic liquid)s» (PIL), although they are solid rather than liquid.
Unexpected properties
Scientists worldwide are currently investigating these PIL for use in different applications, such as batteries and CO2 storage. From their work it is known that PIL can adsorb CO2. "We asked ourselves if we could exploit this property to obtain information on the concentration of CO2 in the air and thereby develop a new type of gas sensor," says Christoph Willa, doctoral student at the Laboratory for Multifunctional Materials.
Willa and Dorota Koziej, a team leader in the laboratory, eventually succeeded by mixing the polymers with specific inorganic nanoparticles that also interact with CO2. By experimenting with these materials, the scientists were able to produce the composite. "Separately, neither the polymer nor the nanoparticles conduct electricity," says Willa. "But when we combined them in a certain ratio, their conductivity increased rapidly."
Chemical changes in the material
It was not only this that astonished the scientists. They were also surprised that the conductivity of the composite material at room temperature is CO2-dependent. "Until now, chemoresistive materials have displayed these properties only at a temperature of several hundred degrees Celsius," explains Koziej. Thus, existing CO2 sensors made from chemoresistive materials had to be heated to a high operating temperature. With the new composite material, this is not necessary, which facilitates its application significantly.
Exactly how the CO2-dependant changes in conductivity were produced is not yet clear; however, the scientists have found indications that a chemical change induced by the presence of CO2 occurs foremost at the interface between the nanoparticles and the polymers at the nanometre scale. "We think that CO2 effects the mobility of the charged particles in the material," says Koziej.
Breathing gauges for scuba divers
With the new sensor, scientists are able to measure CO2 concentration over a wide range - from a concentration of 0.04 volume percent in the earth's atmosphere to 0.25 volume percent.
Existing devices that can detect CO2 measure the optical signal and capitalise on the fact that CO2 absorbs infrared light. In comparison, researchers believe that with the new material much smaller, portable devices can be developed that will require less energy. According to Koziej, "portable devices to measure breathing air for scuba diving, extreme altitude mountaineering or medical applications are now conceivable".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Dorota Koziej
41-446-336-055
Copyright © ETH Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Sports
![]() Surrey reveals its implantable biosensor that operates without batteries May 22nd, 2020
Surrey reveals its implantable biosensor that operates without batteries May 22nd, 2020
![]() Collagen nanofibrils in mammalian tissues get stronger with exercise December 14th, 2018
Collagen nanofibrils in mammalian tissues get stronger with exercise December 14th, 2018
![]() Epoxy compound gets a graphene bump: Rice scientists combine graphene foam, epoxy into tough, conductive composite November 14th, 2018
Epoxy compound gets a graphene bump: Rice scientists combine graphene foam, epoxy into tough, conductive composite November 14th, 2018
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








