Home > Press > Surface matters: Huge reduction of heat conduction observed in flat silicon channels
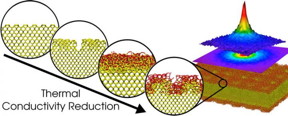 |
| The different circles represent the studied surfaces of the Si membranes: crystalline, rough, flat with native SiO2, and rough with native SiO2. The right image shows a representative thermal map on the membranes upon a localized thermal excitation used to measure the thermal conductivity. CREDIT: ICN2 |
Abstract:
The ability of materials to conduct heat is a concept that we are all familiar with from everyday life. The modern story of thermal transport dates back to 1822 when the brilliant French physicist Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier published his book "Théorie analytique de la chaleur" (The Analytic Theory of Heat), which became a corner stone of heat transport. He pointed out that the thermal conductivity, i.e., ratio of the heat flux to the temperature gradient is an intrinsic property of the material itself.
Surface matters: Huge reduction of heat conduction observed in flat silicon channels
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on April 23rd, 2015The advent of nanotechnology, where the rules of classical physics gradually fail as the dimensions shrink, is challenging Fourier's theory of heat in several ways. A paper published in ACS Nano and led by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (Germany), the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) at the campus of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) (Spain) and the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland (Finland) describes how the nanometre-scale topology and the chemical composition of the surface control the thermal conductivity of ultrathin silicon membranes. The work was funded by the European Project Membrane-based phonon engineering for energy harvesting (MERGING).
The results show that the thermal conductivity of silicon membranes thinner than 10 nm is 25 times lower than that of bulk crystalline silicon and is controlled to a large extent by the structure and the chemical composition of their surface. Combining state-of-the-art realistic atomistic modelling, sophisticated fabrication techniques, new measurement approaches and state-of-the-art parameter-free modelling, researchers unravelled the role of surface oxidation in determining the scattering of quantized lattice vibrations (phonons), which are the main heat carriers in silicon.
Both experiments and modelling showed that removing the native oxide improves the thermal conductivity of silicon nanostructures by almost a factor of two, while successive partial re-oxidation lowers it again. Large-scale molecular dynamics simulations with up to 1,000,000 atoms allowed the researchers to quantify the relative contributions to the reduction of the thermal conductivity arising from the presence of native SiO2 and from the dimensionality reduction evaluated for a model with perfectly specular surfaces.
Silicon is the material of choice for almost all electronic-related applications, where characteristic dimensions below 10 nm have been reached, e.g. in FinFET transistors, and heat dissipation control becomes essential for their optimum performance. While the lowering of thermal conductivity induced by oxide layers is detrimental to heat spread in nanoelectronic devices, it will turn useful for thermoelectric energy harvesting, where efficiency relies on avoiding heat exchange across the active part of the device.
The chemical nature of surfaces, therefore, emerges as a new key parameter for improving the performance of Si-based electronic and thermoelectric nanodevices, as well as of that of nanomechanical resonators (NEMS). This work opens new possibilities for novel thermal experiments and designs directed to manipulate heat at such scales.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Clivia M. Sotomayor Torres
34-937-372-607
Copyright © Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
NEMS
![]() IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
IEDM - CEA-Leti Will Present 11 Papers and Host Workshop on Disruptive Technologies for Data Management November 7th, 2018
![]() UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
UT engineers develop first method for controlling nanomotors: Breakthrough for nanotechnology as UT engineers develop first method for switching the mechanical motion of nanomotors September 21st, 2018
![]() Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
Nano-kirigami: 'Paper-cut' provides model for 3D intelligent nanofabrication July 13th, 2018
![]() One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
One string to rule them all April 17th, 2018
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








