Home > Press > Copper shines as flexible conductor
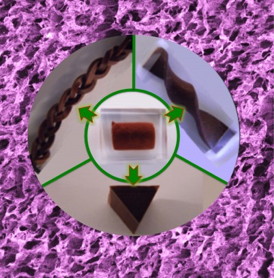 |
| Sensors made with copper are cheap, light, flexible and highly conductive. |
Abstract:
Bend them, stretch them, twist them, fold them: modern materials that are light, flexible and highly conductive have extraordinary technological potential, whether as artificial skin or electronic paper.
Copper shines as flexible conductor
Victoria, Australia | Posted on August 29th, 2014Making such concepts affordable enough for general use remains a challenge but a new way of working with copper nanowires and a PVA "nano glue" could be a game-changer.
Previous success in the field of ultra-lightweight "aerogel monoliths" has largely relied on the use of precious gold and silver nanowires.
By turning instead to copper, both abundant and cheap, researchers at Monash University and the Melbourne Centre for Nanofabrication have developed a way of making flexible conductors cost-effective enough for commercial application.
"Aerogel monoliths are like kitchen sponges but ours are made of ultra fine copper nanowires, using a fabrication process called freeze drying," said lead researcher Associate Professor Wenlong Cheng, from Monash University's Department of Chemical Engineering.
"The copper aerogel monoliths are conductive and could be further embedded into polymeric elastomers - extremely flexible, stretchable materials - to obtain conducting rubbers."
Despite its conductivity, copper's tendency to oxidation and the poor mechanical stability of copper nanowire aerogel monoliths mean its potential has been largely unexplored.
The researchers found that adding a trace amount of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) to their aerogels substantially improved their mechanical strength and robustness without impairing their conductivity.
What's more, once the PVA was included, the aerogels could be used to make electrically conductive rubber materials without the need for any prewiring. Reshaping was also easy.
"The conducting rubbers could be shaped in arbitrary 1D, 2D and 3D shapes simply by cutting, while maintaining the conductivities," Associate Professor Cheng said.
The versatility extends to the degree of conductivity. "The conductivity can be tuned simply by adjusting the loading of copper nanowires," he said. "A low loading of nano wires would be appropriate for a pressure sensor whereas a high loading is suitable for a stretchable conductor."
Affordable versions of these materials open up the potential for use in a range of new-generation concepts: from prosthetic skin to electronic paper, for implantable medical devices, and for flexible displays and touch screens.
They can be used in rubber-like electronic devices that, unlike paper-like electronic devices, can stretch as well as bend. They can also be attached to topologically complex curved surfaces, serving as real skin-like sensing devices, Associate Professor Cheng said.
In their report, published recently in ACS Nano, the researchers noted that devices using their copper-based aerogels were not quite as sensitive as those using gold nanowires, but had many other advantages, most notably their low-cost materials, simpler and more affordable processing, and great versatility.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Glynis Smalley
61-408-027-848
Copyright © Monash University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Flexible Electronics
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








