Home > Press > A smashing new look at nanoribbons: Rice University lab unzips nanotubes into ribbons by shooting them at a target
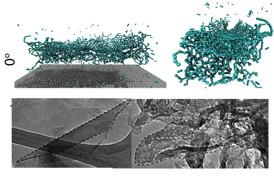 |
| Molecular simulations and electron microscope images show what happens to a carbon nanotube when the end of it strikes a target directly at about 15,000 miles per hour. Rice University researchers found the nanotubes split into useful nanoribbons. Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes "unzipped" into graphene nanoribbons by a chemical process invented at Rice University are finding use in all kinds of projects, but Rice scientists have now found a chemical-free way to unzip them.
A smashing new look at nanoribbons: Rice University lab unzips nanotubes into ribbons by shooting them at a target
Houston, TX | Posted on June 30th, 2014The Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan discovered that nanotubes that hit a target end first turn into mostly ragged clumps of atoms. But nanotubes that happen to broadside the target unzip into handy ribbons that can be used in composite materials for strength and applications that take advantage of their desirable electrical properties.
The Rice researchers led by graduate student Sehmus Ozden reported their finding in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
The result was a surprise, Ozden said. "Until now, we knew we could use mechanical forces to shorten and cut carbon nanotubes. This is the first time we have showed carbon nanotubes can be unzipped using mechanical forces."
The researchers fired pellets of randomly oriented, multiwalled carbon nanotubes from a light gas gun built by the Rice lab of materials scientist Enrique Barrera with funding from NASA. The pellets impacted an aluminum target in a vacuum chamber at about 15,000 miles per hour. When they inspected the resulting carbon rubble, they found nanotubes that smashed into the target end first or at a sharp angle simply deformed into a crumpled nanotube. But tubes that hit lengthwise actually split into ribbons with ragged edges.
"Hypervelocity impact tests are mostly used to simulate the impact of different projectiles on shields, spacecraft and satellites," Ozden said. "We were investigating possible applications for carbon nanotubes in space when we got this result."
The effect was confirmed through molecular simulations. They showed that when multiwalled tubes impact the target, the outer tube flattens, hitting the inside tubes and unzipping them in turn. Single-wall nanotubes do just the opposite; when the tube flattens, the bottom wall hits the inside of the top wall, which unzips from the middle out to the edges.
Ozden explained that the even distribution of stress along the belly-flopping nanotube, which is many times longer than it is wide, breaks carbon bonds in a line nearly simultaneously.
The researchers said 70 to 80 percent of the nanotubes in a pellet unzip to one degree or another.
Ozden said the process eliminates the need to clean chemical residues from nanoribbons produced through current techniques. "One-step, chemical-free, clean and high-quality graphene nanoribbons can be produced using our method. They're potential candidates for next-generation electronic materials," he said.
Co-authors include Pedro Autreto, a postdoctoral researcher at the State University of Campinas, Brazil, who has a complimentary appointment at Rice; graduate student Chandra Sekhar Tiwary of Rice and the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore; graduate student Suman Khatiwada of Rice; Leonardo Machado and Douglas Galvao of the State University of Campinas; and Robert Vajtai, a senior faculty fellow at Rice. Barrera is a professor of materials science and nanoengineering. Ajayan is Rice's Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science and of chemistry, and chair of the Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering.
The Department of Defense, U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research through a Multidisciplinary University Research Institute grant, and the Brazilian agencies National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel and the São Paulo Research Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,920 undergraduates and 2,567 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6.3-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








