Home > Press > New magnetic behavior in nanoparticles could lead to even smaller digital memories
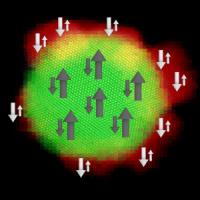 |
| This is a schematic representation of the antiferromagnetic coupling between a magnetic Fe3O4 soft core and a magnetic Mn3O4 hard shell. The image of an electronic high-resolution transmission microscope, superimposed on a map of electronic energy loss spectroscopy, reveals the high quality of the interface with a coherent increase between the two phases.
Credit: UAB |
Abstract:
Electronic devices such as mobile phones and tablets spur on a scientific race to find smaller and smaller information processing and storage elements. One of the challenges in this race is to reproduce certain magnetic effects at nanometre scale.
New magnetic behavior in nanoparticles could lead to even smaller digital memories
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on December 19th, 2013An international collaboration of scientists led by researchers from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Department of Physics and the Institut Catala de Nanociencia i Nanotecnologia, and with the participation of the Universitat de Barcelona, has been able to reproduce in particles measuring 10 to 20 nanometres a magnetic phenomenon of great importance in magnetic devices: the antiferromagnetic coupling between layers.
This phenomenon appears when coupling layers of materials with different magnetic properties, which allows controlling the magnetic behaviour of the whole device. This property has very important technological applications. For example, it forms an important part of data reading systems found in hard drives and in the MRAM memories of computers and mobile devices.
Researchers have managed for the first time to reproduce this phenomenon in nanoscopic materials, measuring a mere few tens of atoms in diameter. They managed to do this by using iron-oxide particles surrounded by a thin layer of manganese-oxide and vice versa: manganese-oxide particles covered by a layer of iron-oxide. The discovery provides an unprecedented control of the magnetic behaviour of nanoparticles, since it permits controlling and easily adjusting their properties without having to manipulate their shape or composition, solely by controlling the temperature and the magnetic fields surrounding it.
"We've been able to reproduce a magnetic behaviour not previously observed in nanoparticles, and this paves the way for miniaturisation up to limits which seemed impossible for magnetic storage and other more sophisticated applications such as spin filters, magnetic codifiers and multi-level recording", explain Josep Nogués, ICREA research professor, and Maria Dolors Baró, professor of Applied Physics.
###
The research, published today in Nature Communications, included the participation of professors Maria Dolors Baró and Santiago Suriñach from the Department of Physics of the UAB; ICREA research professor Josep Nogués, from the Department of Physics of the UAB and ICN2; researchers from the Department of Inorganic Chemistry and from the Department of Electronics at the University of Barcelona (UB); researchers from the Complutense University of Madrid; the Università degli Studi di Firenze, Italy; the St. Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute, Russia; the Stockholm University, Sweden; the NCSR in Greece; the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA; the Miami University, Ohio, USA; and the Argonne National Laboratory, USA.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dolors Baró
34-935-811-657
Copyright © Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








