Home > Press > Looking At and Into the Ultra-Small
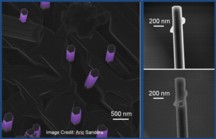 |
| The helium ion microscope has high depth of focus and resolution providing researchers with images of gallium nitride nanowires that would be impossible to produce with electron microscopy. In addition, helium ions provide the ability to etch very precisely. |
Abstract:
NIST is taking a huge step into the ultra-small with the Precision Imaging Facility (PIF) now being outfitted in new Precision Measurement Laboratory on the Boulder campus. The PIF, which houses some of the most advanced imaging instruments in the world, will give researchers the ability to dissect, create, and catalog technologically important materials and devices at the atomic level, and will fill researchers' microscopy and microanalysis needs for years to come. Completion is scheduled for mid-2012.
Looking At and Into the Ultra-Small
Boulder, CO | Posted on June 13th, 2012A suite of four new instruments and supporting equipment "will directly benefit a broad spectrum of NIST/Boulder's already successful projects," says PIF's Aric Sanders of PML's Quantum Electronics and Photonics Division. "In particular, they will impact projects that create advanced quantum sensors, conduct nanowire-based renewable energy metrology, devise chip-scale atomic clocks and nanoscale magnetic devices, and investigate the reliability of nanomaterials."
The specifications for the 3000-square-foot, shared-use facility were determined by a collaboration of groups at NIST/Boulder, including PML's Time and Frequency, Quantum Electronics and Photonics, and Electromagnetics divisions, as well as the Thermophysical Properties and Materials Reliability divisions of NIST's Material Measurement Laboratory.
The PIF's technological capabilities - the most sophisticated available outside certain Department of Energy facilities - will particularly benefit programs which rely on the complicated interworking of nanoscale materials and microfabrication technology that can only be probed by advanced imaging tools. Eventually, the full suite of instruments will include an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope (TEM), a combination focused ion beam/scanning electron beam microscope (FIB/SEM), a helium ion microscope, and a local electrode atom probe (LEAP).
Image of gallium nitride nanowires.
The helium ion microscope has high depth of focus and resolution providing researchers with images of gallium nitride nanowires that would be impossible to produce with electron microscopy. In addition, helium ions provide the ability to etch very precisely. (Click image to enlarge.)
Each instrument offers distinctive advantages for measurement and analysis.
The TEM opens the door to sub-angstrom (1 Å = 10-10 m) resolution imaging necessary for the characterization of crystalline materials used for single photon emitters, nanoscale light sources, and advanced quantum information circuits. The aberration-corrected TEM, the electrons from which pass completely through the specimen and are imaged on the other side, can locally investigate chemical composition, creating the ability to evaluate directly the results of advanced crystal growth techniques needed for the next generation of such devices.
The FIB/SEM combines two functions that together enable highly precise, three-dimensional manipulation and preparation of samples. A focused beam of ions selectively mills devices and materials at nanometer scales, while the sample is also imaged by an SEM. The combination can reveal internal structure in exquisite detail, and provides an indispensable tool for the preparation of samples for the other analytical techniques such as atom probe and transmission electron microscopy.
The helium ion microscope provides a completely new methodology for imaging surfaces of biological and inorganic materials. Because of the nature of helium ion-sample interactions , this tool also provides the ability to pattern samples without the limitations of imposed by electron beam techniques thus opening the path to devices of sub-10 nm sizes with sub-15 nm spacing.
Local-Electrode Atom Probe (LEAP) devices produce the highest spatial resolution currently available for analyzing specimens at the nanoscale. The PIF's LEAP, when installed, will reconstruct analytic volumes atom by atom, revealing the location and chemical composition of structures invisible to other methods. In particular it has a sensitivity to atomic species and location that is unmatched in other analytic instruments. The atom probe is the only microscope that can achieve 1 part per million resolution in chemistry and effectively single atomic spatial resolution. Although averaging techniques can yield higher chemical resolution (1 He atom in 106 Si atoms, for example) they average over a larger area to achieve this. The new LEAPwill offer NIST researchers the ability to investigate, for example, the distribution of dopants in nanoscale semiconductor devices.
The capabilities of these four instruments, coupled with the associated sample preparation and inspection resources also housed in the PIF, provide uniquely powerful abilities to NIST and potentially, through focused collaborations, to the broader scientific community.
Operation of the PIF is modeled on the very successful cooperative Boulder microfabrication facility which has been in existence for many years. In this operational model all projects at NIST Boulder have access to the PIF and the extension and refinement of the facility and its resources evolves continually to meet the needs of NIST's world-class research.
####
About National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
Any mention or image of commercial products within NIST web pages is for information only; it does not imply recommendation or endorsement by NIST.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aric Sanders
303-497-4731
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








