Home > Press > Self-healing electronics could work longer and reduce waste
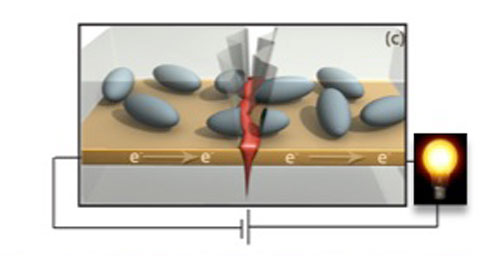 |
| Graphic by Scott White Self-healing electronics. Microcapsules full of liquid metal sit atop a gold circuit. When the circuit is broken, the microcapsules rupture, filling in the crack and restoring the circuit. |
Abstract:
When one tiny circuit within an integrated chip cracks or fails, the whole chip - or even the whole device - is a loss. But what if it could fix itself, and fix itself so fast that the user never knew there was a problem?
Self-healing electronics could work longer and reduce waste
Champaign, IL | Posted on December 20th, 2011A team of University of Illinois engineers has developed a self-healing system that restores electrical conductivity to a cracked circuit in less time than it takes to blink. Led by aerospace engineering professor Scott White and materials science and engineering professor Nancy Sottos, the researchers published their results in the journal Advanced Materials.
"It simplifies the system," said chemistry professor Jeffrey Moore, a co-author of the paper. "Rather than having to build in redundancies or to build in a sensory diagnostics system, this material is designed to take care of the problem itself."
As electronic devices are evolving to perform more sophisticated tasks, manufacturers are packing as much density onto a chip as possible. However, such density compounds reliability problems, such as failure stemming from fluctuating temperature cycles as the device operates or fatigue. A failure at any point in the circuit can shut down the whole device.
"In general there's not much avenue for manual repair," Sottos said. "Sometimes you just can't get to the inside. In a multilayer integrated circuit, there's no opening it up. Normally you just replace the whole chip. It's true for a battery too. You can't pull a battery apart and try to find the source of the failure."
Most consumer devices are meant to be replaced with some frequency, adding to electronic waste issues, but in many important applications - such as instruments or vehicles for space or military functions - electrical failures cannot be replaced or repaired.
The Illinois team previously developed a system for self-healing polymer materials and decided to adapt their technique for conductive systems. They dispersed tiny microcapsules, as small as 10 microns in diameter, on top of a gold line functioning as a circuit. As a crack propagates, the microcapsules break open and release the liquid metal contained inside. The liquid metal fills in the gap in the circuit, restoring electrical flow.
"What's really cool about this paper is it's the first example of taking the microcapsule-based healing approach and applying it to a new function," White said. "Everything prior to this has been on structural repair. This is on conductivity restoration. It shows the concept translates to other things as well."
A failure interrupts current for mere microseconds as the liquid metal immediately fills the crack. The researchers demonstrated that 90 percent of their samples healed to 99 percent of original conductivity, even with a small amount of microcapsules.
The self-healing system also has the advantages of being localized and autonomous. Only the microcapsules that a crack intercepts are opened, so repair only takes place at the point of damage. Furthermore, it requires no human intervention or diagnostics, a boon for applications where accessing a break for repair is impossible, such as a battery, or finding the source of a failure is difficult, such as an air- or spacecraft.
"In an aircraft, especially a defense-based aircraft, there are miles and miles of conductive wire," Sottos said. "You don't often know where the break occurs. The autonomous part is nice - it knows where it broke, even if we don't."
Next, the researchers plan to further refine their system and explore other possibilities for using microcapsules to control conductivity. They are particularly interested in applying the microcapsule-based self-healing system to batteries, improving their safety and longevity.
This research was supported as part of the Center for Electrical Energy Storage, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science. Moore, Sottos and White are also affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the U. of I. Co-authors of the paper included postdoctoral researchers Benjamin Blaiszik and Sharlotte Kramer and graduate students Martha Grady and David McIlroy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1079
Scott White
217-333-1077
Copyright © University of Illinois College at Uraba-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The paper, “Autonomic Restoration of Electrical Conductivity,” is available online:
The paper, “Autonomic Restoration of Electrical Conductivity,” is available online:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Videos/Movies
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
![]() Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Visualizing the invisible: New fluorescent DNA label reveals nanoscopic cancer features March 4th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








