Home > Press > NIST Uncovers Reliability Issues for Carbon Nanotubes in Future Electronics
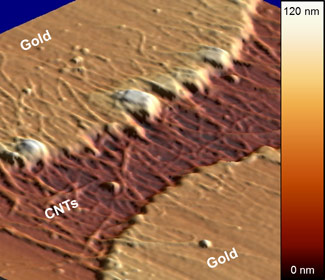 |
| Micrograph of recession and clumping in gold electrodes after NIST researchers applied 1.7 volts of electricity to the carbon nanotube wiring for an hour. The NIST reliability tests may help determine whether nanotubes can replace copper wiring in next-generation electronics. Credit: M. Strus/NIST |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes offer big promise in a small package. For instance, these tiny cylinders of carbon molecules theoretically can carry 1,000 times more electric current than a metal conductor of the same size. It's easy to imagine carbon nanotubes replacing copper wiring in future nanoscale electronics.
NIST Uncovers Reliability Issues for Carbon Nanotubes in Future Electronics
Boulder, CO | Posted on August 17th, 2011But—not so fast. Recent tests at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) suggest device reliability is a major issue.
Copper wires transport power and other signals among all the parts of integrated circuits; even one failed conductor can cause chip failure. As a rough comparison, NIST researchers fabricated and tested numerous nanotube interconnects between metal electrodes. NIST test results, described at a conference this week,* show that nanotubes can sustain extremely high current densities (tens to hundreds of times larger than that in a typical semiconductor circuit) for several hours but slowly degrade under constant current. Of greater concern, the metal electrodes fail—the edges recede and clump—when currents rise above a certain threshold. The circuits failed in about 40 hours.
While many researchers around the world are studying nanotube fabrication and properties, the NIST work offers an early look at how these materials may behave in real electronic devices over the long term. To support industrial applications of these novel materials, NIST is developing measurement and test techniques and studying a variety of nanotube structures, zeroing in on what happens at the intersections of nanotubes and metals and between different nanotubes. "The common link is that we really need to study the interfaces," says Mark Strus, a NIST postdoctoral researcher.
In another, related study published recently,** NIST researchers identified failures in carbon nanotube networks—materials in which electrons physically hop from tube to tube. Failures in this case seemed to occur between nanotubes, the point of highest resistance, Strus says. By monitoring the starting resistance and initial stages of material degradation, researchers could predict whether resistance would degrade gradually—allowing operational limits to be set—or in a sporadic, unpredictable way that would undermine device performance. NIST developed electrical stress tests that link initial resistance to degradation rate, predictability of failure and total device lifetime. The test can be used to screen for proper fabrication and reliability of nanotube networks.
Despite the reliability concerns, Strus imagines that carbon nanotube networks may ultimately be very useful for some electronic applications. "For instance, carbon nanotube networks may not be the replacement for copper in logic or memory devices, but they may turn out to be interconnects for flexible electronic displays or photovoltaics," Strus says.
Overall, the NIST research will help qualify nanotube materials for next-generation electronics, and help process developers determine how well a structure may tolerate high electric current and adjust processing accordingly to optimize both performance and reliability.
* M.C. Strus, R.R. Keller and N. Barbosa III. Electrical reliability and breakdown mechanisms in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Paper presented at IEEE Nano 2011, Portland, Ore., Aug. 17, 2011.
** M.C. Strus, A.N. Chiaramonti, Y.L. Kim, Y.J. Jung and R.R. Keller. Accelerated reliability testing of highly aligned single-walled carbon nanotube networks subjected to dc electrical stressing. Nanotechnology 22 pp. 265713 (2011).
####
About NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
303-497-4880
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








