Home > Press > Single-molecule technique captures calcium sensor in action
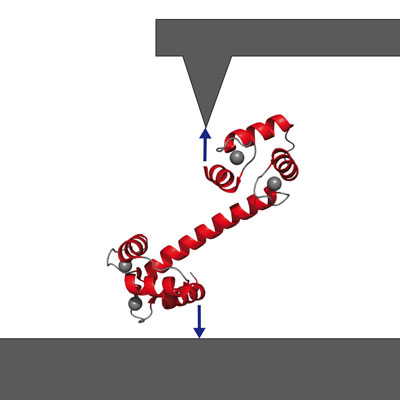 |
| Getting a handle on signaling protein calmodulin via atomic-force spectroscopy. (Image: M. Rief, TUM Dept. of Physics) |
Abstract:
It's well known that the protein calmodulin specifically targets and steers the activities of hundreds of other proteins - mostly kinases - in our cells, thus playing a role in physiologically important processes ranging from gene transcription to nerve growth and muscle contraction. But just how it distinguishes between target proteins is not well understood.
Single-molecule technique captures calcium sensor in action
München, Germay | Posted on August 10th, 2009Methods developed by biophysicists at the Technische Universität München (TUM) have enabled them to manipulate and observe calmodulin in action, on the single-molecule scale. In recent experiments, as they report in the early edition of PNAS, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, they compared the sequences of structural and kinetic changes involved in binding two different kinases. The results reveal new details of how calmodulin binds and regulates its target proteins.
A so-called signaling protein and "calcium sensor," calmodulin gives start and stop signals for a great number of intracellular activities by binding and releasing other proteins. Calmodulin can bind up to four calcium ions, and the three-dimensional spatial structure of calmodulin varies with the number of calcium ions bound to it. This structure in turn helps to determine which amino acid chains - peptides and proteins - the calmodulin will bind.
Techniques such as X-ray structural analysis offer snapshots, at best, of steps in this intracellular work flow. But single-molecule atomic-force spectroscopy has opened a new window on such dynamic processes.
Professor Matthias Rief and colleagues at the Technische Universität München had previously shown that they could fix a single calmodulin molecule between a surface and the cantilever tip of a specially built atomic-force microscope, expose it to calcium ions in solution, induce peptide binding and unbinding, and measure changes in the molecule's mechanical properties as it did its work.
"What is special about our technique," Rief says, "is that we can work directly in aqueous solution. We can make our measurements in exactly the conditions under which the protein works in its natural environment. So we can directly observe how the calmodulin snatches the amino acid chain and folds itself, to hold its target fast." Measuring the force needed to bend the calmodulin molecule out of its stable condition at any given moment enables the researchers to compute the energies associated with binding both the calcium ions and the amino acid chains. And by following changes in the molecule's mechanical properties over time, they also can determine how long a protein fragment remains bound.
The results Rief and biophysicist Jan Philipp Junker report in the early edition of PNAS show that their approach also enables detailed comparative studies of binding sequences for different target proteins. The target sequences observed in these experiments are called skMLCK and CaMKK. Rief and Junker used mechanical force - actually pulling on complexes of calmodulin and the target peptides at rates of 1 nanometer per second or less - to slow down the processes to observable time scales and to clearly separate the individual unbinding steps.
"By applying mechanical force," Junker says, "we are able to dismantle the calmodulin-target peptide complex with surgical precision. Using conventional methods, this would be very difficult to do."
Among the detailed insights this approach made accessible are the hierarchy of folding and target binding, the sequence of unbinding events, and target-specific differences in terms of what is called cooperative binding.
Full bibliographic information
"Single-molecule force spectroscopy distinguishes target binding modes of calmodulin," by Jan Philipp Junker and Matthias Rief, published in the online Early Edition of PNAS, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, for the week of August 10, 2009.
####
About Technische Universität München
Das Studenten- und Mitarbeiterportal der Technischen Universität München ist Teil des Projekts myTUM unter der Leitung von Dr. Thomas Wagner, einem Projekt zur Realisierung eines zentralen Hochschulportals für Forschung und Lehre, sowie der Einführung eines fortschrittlichen, vollständig dezentralisierten Informationsmanagements.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Public Relations Team
Arcisstr. 19
80333 München
Tel.: +49.89.289.22778
Fax: +49.89.289.23388
Copyright © Technische Universität München
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








