Home > Press > Polymers “battered” with nanoparticles could create self healing paints and clever packaging
 |
Abstract:
Research chemists at the University of Warwick have devised an elegant process which simply and cheaply covers small particles of polymer with a layer of silica-based nanoparticles. The final result provides a highly versatile material that can be used to create a range of high performance materials such as; self healing paints, and clever packaging that can be tailored to let precise levels of water, air or both pass in a particular direction.
Polymers “battered” with nanoparticles could create self healing paints and clever packaging
UK | Posted on November 25th, 2008The research, led by Dr Stefan Bon of University of Warwick's Department of Chemistry, has created a "soap free emulsion polymerization process" which makes colloid particles of polymer dispersed in water and in one simple step introduces nanometre sized silica based particles to the mix. These silica based nanoparticles (about 25 nanometre in size) then coats the polymer colloids with a layer "battering" it almost like a fish can be battered in bread crumbs.
This process creates a very versatile polymer latex product. It can be used to create scratch resistant paints in which the scratches heal themselves. It can be fine tuned to produce polymer based packaging which will allow water or air to pass through the packaging in tailored ways. The resultant rough textured spherical shapes also lend themselves to the creation of sheets with polymer that present much more surface area than usual allowing more efficient interaction with other materials.
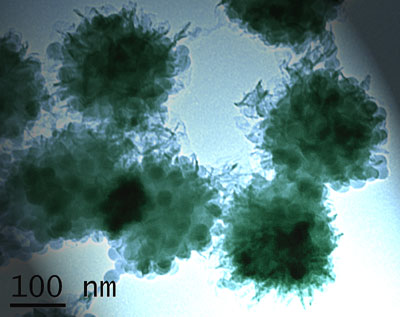
The versatility of this process did not stop there. By exposing the material to a second simple step which deposited another polymer layer on top of the already silica based nanoparticles "battered" polymers the researchers were able to produce particles with an even greater range of properties and uses. The image shows such a multi-layered polymer colloid and was taken with a transmission electron microscope. Click on the picture to be taken to a larger hi res version.
Industrialists will be interested not just in the versatility of the end product but the ease and cost effectiveness of the process. The Warwick research team has worked on a number of other processes that coated polymers in forms of protection but they all required a number of steps to produce the end result. This new process cuts dramatically the time needed to create such materials and its single step can already be produced on a mass scale with currently used industrial equipment. The amount of material that one can harvest from the process will also impress industrialists as the Warwick team showed that the useful product can easily be made up to around 45% of the volume of each water-based solution used in their process. This compares with figures of as of little as 1 to 10 % for comparable multi-step processes that make these complex particles.
The research paper by Patrick J. Colver, Catheline A. L. Colard, and Stefan A. F. Bon at the University of Warwick is entitled Multilayered Nanocomposite Polymer Colloids Using Emulsion Polymerization Stabilized by Solid Particles in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. See pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja807242k
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr Stefan Bon
Associate Professor of Polymer Chemistry
Department of Chemistry
University of Warwick
Tel: 024 7657 4009
Web : www.stefanbon.eu
Peter Dunn
Press and Media Relations Manager
Communications Office
University House
University of Warwick
Coventry CV4 8UW
Tel: 024 76 523708
or 07767 655860
Copyright © University of Warwick
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








