Home > Press > Nanonitrator: novel enhancer of inorganic nitrate protective effects, predicated on swarm learning approach
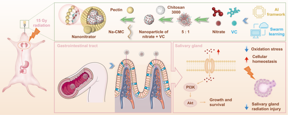 |
| A swarm learning-based drug combination prediction system identifying vitamin C as the optimal drug to be combined with sodium nitrate. This combination improved the bioavailability of sodium nitrate and exerted synergistic effects. Subsequently, the team used microencapsulation technology to prepare a nanoparticle named Nanonitrator, with sodium nitrate and vitamin C as its primary components. Nanonitrator prevented tissue damage in a model of radiation-induced salivary gland injury, verifying their improved efficacy over that of sodium nitrate alone. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Radiotherapy is currently the main form of treatment for head and neck malignancies such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Within the radiation field of a tumor, salivary glands frequently suffer substantial damages following irradiation, resulting in xerostomia and a series of oral syndromes, which seriously impact the quality of patients' lives.
Nanonitrator: novel enhancer of inorganic nitrate protective effects, predicated on swarm learning approach
Beijing, China | Posted on May 12th, 2023In 1998, the research team led by Prof. Songlin Wang established a model of miniature pigs to simulate clinical salivary gland injuries induced by radiation in the head and neck region. The model was employed in a series of studies on the mechanism of radiation-induced salivary gland injuries as well as functional reconstruction of the damaged glands. The team found that exogenous inorganic nitrate supplementation could significantly protect the morphology and function of the salivary glands from radiation injury, suggesting a novel mode of prevention and treatment.
Most existing experimental studies on inorganic nitrate therapy are based on oral administration, including the addition of nitrates to food and drinking water. Orally administered nitrates have low bioavailability, rapid metabolism, and high fluctuation in vivo, making it difficult to achieve pharmacodynamically active concentrations. To resolve these issues and facilitate clinical applications, the team has successfully developed a drug combination prediction system based on swarm learning. Using a deep learning model, the system was trained on drug-pathway interaction data to construct a drug-pathway network. A graph convolutional neural network was used to construct a drug-target network to uncover optimal drug combinations. The system was used to successfully identify vitamin C as the optimal drug for co-administration with sodium nitrate. This finding provides new ideas and methods for drug co-administration, with important clinical implications for the prevention of various diseases.
From this, the optimal nitrate-to-vitamin C ratio was determined using microencapsulation technology for screening and optimization of the controlled release formulation. Thereby a hydrophobic nanodrug named Nanonitrator was prepared, using a core material solution containing sodium nitrate, vitamin C, and chitosan 3000, whereas sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Na-CMC) and pectin were used as wall materials. The core and wall materials were mixed, lyophilized, and crushed into a powder form. The various pH values of gastrointestinal solutions tested in vitro confirmed that Nanonitrator is suitable in oral dosage forms.
Due to their ability to significantly enhance the signal transduction of the PI3K-Akt pathway, Nanonitrator exhibited better effects in maintaining intracellular homeostasis than sodium nitrate alone or sodium nitrate combined in a physical mixture with vitamin C at equivalent oral doses. Nanonitrator reduced radiation-induced oxidative stress in salivary gland cells, reduced ROS content, maintained cellular calcium homeostasis, protected mitochondrial morphology and function, and decreased the number of apoptotic cells.
These results suggest that Nanonitrator could be developed as a novel therapy of multiple applications, with the potential to play an important role in the prevention and treatment of related chronic diseases. Moreover, this study provides new ideas for the development of novel drugs based on inorganic salts.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Expert Contacts
Prof. Xiaogang Wang
School of Engineering Medicine, Beihang University
Prof. Yuji Wang
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Capital Medical University
Prof. Songlin Wang
Capital Medical University
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








