Home > Press > Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI
 |
| A team of Greek academic researchers and California entrepreneurs benchmarked their Silicon Photonic (SiPho) neural network technology against processing unit currently on the market and six-year-old technology with projections. CREDIT Authors of publication |
Abstract:
Artificial intelligence (AI) models are essential for sophisticated image classification, the most important part of digital analysis. The researchers who recently published “Universal Linear Optics Revisited: New Perspectives for Neuromorphic Computing with Silicon Photonics” have moved the needle for image classification. The speeds they’ve achieved on a new chip platform (silicon photonics) using the computational power of neural networks is impressive.
Light meets deep learning: computing fast enough for next-gen AI
Piscataway, NJ | Posted on March 24th, 2023Nonetheless, pay attention here to the modal auxiliary verb “can.” Just because something can be done, questions remain. Will it be fast enough? Will it have sufficient accuracy? How energy efficient is it? Is the chip large and unwieldly? This research tackles them all.
One of the attributes of AI is that you can use it at the edge of the physical network; in a camera for example. A camera on a drone is an even better example. To enable a drone with AI, you want the on-board AI chip to be powerful, but energy efficient, small and lightweight, and able to do lots of complex math at lightning speed. That way, the drone can alert humans when something untoward is detected (cancer, a saboteur, damage to a train-track).
Meanwhile, in Greece, researchers have built a neuromorphic photonic processor computing at a speed of 50 GHz that is capable to classify images with ~95% accuracy. Let’s break this down, starting with the photonic part.
After Silicon Electronics? Silicon Photonics.
AI processor chips often start life as graphic processing units (GPUs) for high-end video games or tensor processing units (TPUs) which are specifically designed for neural networks, meaning computation mimicking the human brain. (Except that they like linear algebra!) However conventional processors use silicon electronics as the physical platform, which is reaching quantum limitations.
Switching from electrons to photons increases computational ability because the speed of light is so much faster than the speed of electrons. It’s more energy efficient too. The “wires” don’t heat up. The physics of light can be used for matrix-vector multiplication operations, the computational backbone of neural networks.
After Conventional Math? Neuromorphic Computing with Trillions of Operations per Second
Now the neuromorphic part. The Greek research team, along with Celestial AI, developed a novel design for the chip using a crossbar layout. The layout outperforms the state-of-the-art photonic counterparts in terms of scalability, technical versatility, ease of programming and error tolerance. Said differently, by combining the crossbar layout’s architectural benefits with SiGe electro-absorption modulators employed in their first prototype, the researchers project that a purely optical implementation can perform trillions of matrix-vector multiplications per second, without sacrificing the processing accuracy, while consuming very low power.
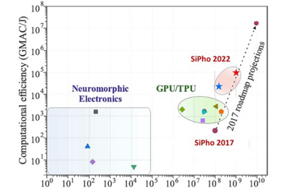
Compared with six years ago, silicon photonics is in a much better position to pull neural morphic processors from their currently low computational and physical size (footprint) efficiency to less unwieldy. Notice in Figure 1 the placement of IBM’s TrueNorth chip, Intel’s Loihi chip, the HICANN (High Input Count Analog Neural Network) chip from Germany’s Heidelberg University and Stanford U’s neurogrid device. Compare it to the crossbar-layout chips discussed here, which are falling right along silicon photonics roadmap in terms of computation and size efficiency. The synergy of powerful photonics with the novel crossbar architecture can enable next generation neuromorphic computing engines. Let’s change that that modal auxiliary verb to “will.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Kristen Mahan
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Expert Contact
Kristen Mahan
IEEE
Office: 17322723320
Copyright © Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Artificial Intelligence
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








