Home > Press > Scientists reveal the effect of Cu(I) structure on quantum sieving for hydrogen isotope separation
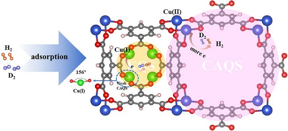 |
| The separation mechanism of D2/H2 mixture in Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC. CREDIT HU Xiaoyu |
Abstract:
Recently, a research team led by Prof. CHEN Changlun from Institute of Plasma Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences, studied Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC, a kind of hydrogen isotope separation material and proved its crucial role in tuning quantum sieving without a complex structural design, which provided a new strategy for the intelligent design of highly efficient isotope systems.
Scientists reveal the effect of Cu(I) structure on quantum sieving for hydrogen isotope separation
Hefei, China | Posted on February 10th, 2023The result was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
High pure deuterium (D2) is an important industrial and scientific gas, which has been widely used as an irreplaceable raw material, neutron moderator, isotopic tracer, and in other fields. Despite the huge demand for it, the mole fraction of natural deuterium is only up to 0.0156% of natural hydrogen in the oceans. Moreover, D2 and its isotope (H2 or T2) molecules have almost identical classical dimensions, associated with very similar physicochemical properties, and the separation of hydrogen isotope mixtures in high purity has been considered as one of the greatest difficulties and challenges in modern separation technology.
In this study, HKUST-1 crystals in the presence of hydroquinone were reduced to construct Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC, featured by dual micropore size distribution and mixed-valence of Cu metal, and had been chosen to study H2/D2 separation in detail.
The study showed that unique Cu(I) and Cu(II) coordination network of Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC could significantly facilitate D2/H2 isotope separation. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicated that the introduction of Cu(I) macrocycles in the framework decreased the pore size and further led to relatively enhanced interaction of H2/D2 molecules on Cu(II) sites. The significantly enhanced selectivity of Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC at 30 K was mainly attributed to the synergistic effect of kinetic quantum sieving (KQS) and chemical affinity quantum sieving (CAQS).
In addition, a large angle of 156° for the O-Cu(I)-O configuration in Cu(I)Cu(II)-BTC exhibited weak binding strength of hydrogen adsorption since the dz2 orbital and small positive of Cu(I) couldn't effectively participate in the hydrogen interaction, and didn't show a strong CAQS effect at above liquid nitrogen temperature.
This research verified the effect of Cu(I) structure in D2/H2 separation. "We believe that this study will provide a new strategy for reasonable design of porous materials with OMSs at highly efficient isotope and gas separation systems," said HU Xiaoyu, first author of the paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Weiwei Zhao
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Office: 86-551-655-91206
Copyright © Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








