Home > Press > Rapid fluorescent mapping of electrochemically induced local pH changes
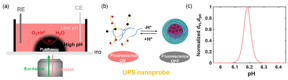 |
| Ultra-pH-sensitive (UPS) probe molecules used in this work hold a deprotonation-induced micellization equilibrium that is responsible for the fluorescent quenching, where the red dots are the fluorophores and black ones the quencher on the copolymeric chains, and its narrow response window of between 6.1 and 6.3 in standard phosphate-buffered salines. The y-axis refers to the normalized (to the maximum) differentiation of fluorescent (FL) intensity with respect to pH, directly showing the sharpness of the probe's response. Art by Wang’s group. CREDIT Beijing Zhongke Journal Publising Co. Ltd. |
Abstract:
This study is led by Dr. Wei Wang (Nanjing University). Protons broadly participate in important electrocatalysis as long as the aqueous reaction involves at any elementary step the molecules (e.g. superoxide radical, hydroquinone) and surfaces (e.g. metal oxide, functionalized carbon materials) that can be protonated or deprotonated. On this basis, the detection and monitoring of protons may provide quantitative insights into the kinetics of the electron transfer processes, which is particularly useful for evaluating and understanding the performance of the catalysts of interest. However, the proton gradients only develop over tens or hundreds of microns in the distance of a stationary solution due to the slow nature of diffusion as compared to that occurring at a hydrodynamic electrode surface and the occurrence of natural convection in practice. This poses a difficulty in measuring the confined concentration profiles.
Rapid fluorescent mapping of electrochemically induced local pH changes
Beijing, China | Posted on December 9th, 2022Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) is recognized to overcome the limitation by using a delicately fabricated ion-selective microelectrode probe operated alternatively with amperometry (or a nonoptical shear force detection system, or coupled with optical microscopy) for measuring tip-substrate distances and with potentiometry for measuring the local pH so as to construct the pH profiles. SECM has also been designed to outline the local ionic activity at constant heights of the studied electrode surface under voltammetric mode. That said, whilst the spatial resolution is mainly determined by the size and geometry of the electrode tip, the technique can only give dynamic measurements at a typical time resolution of minutes as limited by not only the frame size but also the fact that the desired measurement accuracy requires long resident times of the tip electrode intrinsically for reaching the steady states of electrode processes (e.g., capacitive charging, diffusion) after the onset.
Alternatively, with aid of probe molecules, fluorescent microscopy has proven to be well-suited for electrochemically induced local pH mapping. In particular, confocal laser scanning microscopy has been demonstrated to depict the pH gradient in the vertical dimension normal to the studied surface and quantitatively map the distribution with a submicron resolution. The technique is later shown to identify areas with fast electrode kinetics of microelectrode arrays and to evaluate the activities of varied metal catalysts. Only recently, the temporal measurement of the advanced optical method has just been achieved with a resolution of 40 seconds as it relies on laser scanning; the time resolution is essential to study the catalytic kinetics of an electrode reaction.
Whilst confocal scanning microscopy holds the important advantage of minimized background interference and thus being quantitative that is consistent with diffusion theory, certain applications such as comparing the catalytic performance of different electrocatalysts may only require a semi-quantitative but efficient measurement. Wide-field microscopy takes advantage of its relatively simple imaging principle for readily measuring two-dimensional concentration profiles of ions of interest that can reflect the kinetics of studied processes in a quantitative way. For instance, they have recently demonstrated the wide-field operando imaging of the dynamic heterogeneous processes of methanol electro-oxidation/formaldehyde formation and oxygen waves closely associated with bacterial metabolism. With the ease of operation, this efficient technique can be revisited for measuring proton gradients developed over a limited space. To further pursue fast imaging with good sensitivity, they adopt an ultra-pH-sensitive (UPS) polymeric fluorescent nanoprobe which can respond sharply within 0.2 pH units. The invented probe has been developed to successfully monitor with exceptional precision and resolve the complicated multistep process of endosome maturation and to target specific endocytic organelles, where only subtle but insightful pH fluctuation occurs in the living cells. In this sense, they present in this contribution a wide-field microscopic method based on the UPS probe to rapidly (<1 second) depict the pH distribution local to a catalyst array of platinum nanoparticles. The short imaging time means an extremely low concentration change (in the order of nanomolar) to be detected, highlighting the use of the nanoprobe that can resolve pH changes of even less than 0.01 unit at around neutral pH.
In this work, they apply an ultra-pH-sensitive polymeric fluorescent probe to achieve electrochemical imaging at the subsecond timescale of local pH changes induced by an electrocatalytic process. The corresponding concentration changes of protons are in the order of nanomolar and are therefore considered unlikely to be imaged using fluorescent microscopy with conventional small-molecule probes. Even though not fully quantitative as compared to the confocal laser scanning microscopy with a minimised excitation volume, the methodology presented can be useful for comparative imaging of heterogeneous reactions involving pH changes. Different from directly studying fast electron transfer at an electrode surface using wide-field optical microscopy their work shows how the imaging of mass transport can be usefully resolved for the field of electrocatalysis.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
LIngshu Qian
Beijing Zhongke Journal Publising Co. Ltd.
Expert Contact
Wei Wang
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center (ChemBIC), Nanjing University,China
Copyright © Beijing Zhongke Journal Publising Co. Ltd.
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Chemistry
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








