Home > Press > High-speed random number generation using self-chaotic microcavity lasers
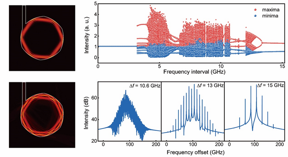 |
| Bifurcation of the extrema for the temporal output waveform versus dual-mode frequency interval (upper right) and ptical spectra of chaos, period-two, and period-one states at mode frequency interval Δf =10.6, 13, and 15 GHz, respectively (lower right). CREDIT by Chun-Guang Ma, Jin-Long Xiao, Zhi-Xiong Xiao, Yue-De Yang, and Yong-Zhen Huang |
Abstract:
Random numbers are crucial in the generation of cryptographic keys for classical and quantum cryptography systems, the reliability of modern networked society, and stochastic simulation, etc. High-bandwidth chaotic semiconductor lasers have been widely investigated for the high-rate generation of random numbers. However, traditional approaches for chaotic lasers with an external feedback have drawbacks of time-delay signature, sensitivity to the parameters of the perturbations and complex adjustment for realization of chaotic output. Hence, a chaotic solitary laser without external perturbations is a prominent configuration for random number generation due to its robust and simple scheme.
High-speed random number generation using self-chaotic microcavity lasers
Changchun, China | Posted on August 26th, 2022In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Yong-Zhen Huang from State Key Laboratory of Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing China, and Center of Material Science and Optoelectronic Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, have proposed a novel approach to manipulate the temporal output of a solitary semiconductor microlaser by nonlinearly coupling of two transverse modes inside the microcavity. Chaotic output is realized from the total output of the deformed microcavity laser without external optical or electric perturbations, which allows to form a simple, small and robust random signal source. Circur-sided hexagonal microresonator (CSHM) was designed to enhance passive mode Q factors for realize dual mode lasing with adjusted frequency interval. Nonlinear dynamical states including period-oscillation states and chaotic state were realized using a solitary CSHM laser. Physical random numbers at 10 Gb/s, which was limited by the used instruments, verified by statistical tests were obtained directly from the total output intensity of the microlaser. The solitary microcavity laser with chaotic total output intensity provides a simple and robust scheme for high-speed random number generation.
A rate equation model based on field equations is set up to account the internal mode interaction including mode coupling. Dual-mode lasing of the fundamental and the first order transverse modes guarantees strong carrier oscillation inside the laser cavity due to mode beating, which enhances the mode interaction. Chaotic dual-mode lasing laser is predicted using the rate equation without external perturbation. These scientists summarize another principle of their lasers:
“In a dual-mode lasing microlaser, mode beating can lead to oscillations of the photon density and carrier density caused by stimulated emission, especially as the mode interval is close to the laser relaxation oscillation frequency. The oscillation of the carrier density will result in side peaks for lasing modes as under external electric modulation, and lead to nonlinear coupling for the two lasing modes because the oscillation frequency is the frequency interval of the two lasing modes.”
“The procedure in revealing the underlying mechanism of the internal interaction between two transverse modes gives a new understanding of the nonlinear dynamical process in the semiconductor microlasers” they added.
“Although the random bits generated at a bit rate of 10 Gbit s-1 (5 GS s-1 × 2 bits) is not much high, which is mainly limited by the instruments used in the test, we expect to realize higher bandwidth of random bits .”
“There is still much room to improve the random number rate of spontaneous chaotic microcavity lasers. we have effectively improved the chaotic bandwidth of chaotic lasers through the optimal design of resonant cavity, which is expected to generate higher rate physical random numbers under higher bandwidth chaotic signals. In the future, with the development of optoelectronic integration technology, spontaneous chaotic lasers are expected to achieve convenient and portable miniaturized random number generators.” the scientists forecast.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Expert Contact
Yong-Zhen Huang
Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Copyright © Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








