Home > Press > Study reveals new mode of triggering immune responses
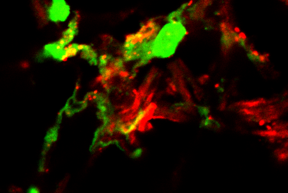 |
| Confocal microscopy image shows that DNA (green) and the chemokine CXCL4 (red) colocalize (indicated by yellow areas) during inflammatory responses in the skin. CREDIT Barrat lab |
Abstract:
Small proteins, called chemokines, that direct immune cells toward sites of infection can also form DNA-bound nanoparticles that can induce chronic, dysfunctional immune responses, according to a new study by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS). The surprising discovery of this new activity for this well-studied class of immune signaling molecules could shed light on some types of immune disorders.
Study reveals new mode of triggering immune responses
New York, NY | Posted on July 15th, 2022The study, published May 31 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, reveals an entirely new mode of triggering the immune system, through which chemokine-DNA nanoparticles can induce inflammation. Results in preclinical models suggest that this mechanism may play a central role in autoimmune diseases such as scleroderma and lupus.
The work was part of the scientists' ongoing efforts to understand scleroderma, an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation and hardening of the skin. “We had a project looking at scleroderma and it was shown by us and others a few years ago that patients with this condition have an elevated level of the chemokine CXCL4 in their blood,” said senior author Dr. Franck Barrat, professor of microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the Michael Bloomberg Chair and senior scientist at HSS. “But the role of this chemokine in disease is unclear and we didn’t expect the chemokine to provoke this particular immune response.”
In setting up controls for one of their experiments, Dr. Barrat’s team, including first author, Dr. Yong Du, a postdoctoral associate in microbiology and immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine and a member of the HSS Research Institute, discovered that CXCL4 and several other chemokines could induce immune cells called plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) to produce interferon-alpha. Surprisingly, the induction appeared to be independent of known chemokine receptors, indicating that these molecules were activating the immune cells through some previously unknown mechanism.
Subsequent experiments revealed that the chemokines can bind pieces of DNA to form nanoparticles, which then bypass the cells’ chemokine receptors to induce interferon production directly. Tests in mouse models of skin inflammation suggest that this mechanism could account for the chronic immune activation that underlies scleroderma and other autoimmune diseases. The results also suggest that different DNA-chemokine nanoparticles could underlie different diseases. For example, while CXCL4 appears to be important in scleroderma, another chemokine, CXCL10, may perform a similar function in lupus.
Dr. Barrat believes that the DNA-chemokine nanoparticles are likely an essential component of the body’s wound healing system. “Following a skin injury, such as if you cut yourself, dendritic cells infiltrate the skin and create an inflammatory environment to allow for proper closing of the wound. Our findings suggest that these cells do not need to see a pathogen—a virus or bacterium—and can directly sense self-DNA,” he said. “And that inflammation is helping to recruit other cells of the immune system.” In autoimmune disease, the process goes awry, producing a chronic inflammatory state that ultimately damages tissue instead of healing it.
The researchers also collaborated on a related study, published June 14 in Nature Communications, that shows that CXCL4 can induce a similar inflammatory response in monocytes, another important class of immune cells. Taken together, the findings point toward possible strategies to shut down autoimmunity without interfering with normal immune responses.
“It tells you the type of response that you have to stop, not necessarily at the DNA-chemokine level, but potentially more downstream in the cells themselves,” Dr. Barrat said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Eliza Powell
Weill Cornell Medicine
Copyright © Weill Cornell Medicine
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








