Home > Press > ‘Life-like’ lasers can self-organise, adapt their structure, and cooperate
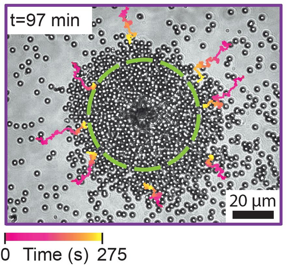 |
| Microparticles clustering around a Janus particle. The dashed line delineates the lasing area, and the pink/yellow lines show the tracks of several microparticles CREDIT Imperial College London |
Abstract:
By mimicking features of living systems, self-organising lasers could lead to new materials for sensing, computing, light sources and displays.
‘Life-like’ lasers can self-organise, adapt their structure, and cooperate
London, UK | Posted on July 15th, 2022While many artificial materials have advanced properties, they have a long way to go to combine the versatility and functionality of living materials that can adapt to their situation. For example, in the human body bone and muscle continuously reorganise their structure and composition to better sustain changing weight and level of activity.
Now, researchers from Imperial College London and University College London have demonstrated the first spontaneously self-organising laser device, which can reconfigure when conditions change.
The innovation, reported in Nature Physics, will help enable the development of smart photonic materials capable of better mimicking properties of biological matter, such as responsiveness, adaptation, self-healing, and collective behaviour.
Co-lead author Professor Riccardo Sapienza, from the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: “Lasers, which power most of our technologies, are designed from crystalline materials to have precise and static properties. We asked ourselves if we could create a laser with the ability to blend structure and functionality, to reconfigure itself and cooperate like biological materials do.
“Our laser system can reconfigure and cooperate, thus enabling a first step towards emulating the ever-evolving relationship between structure and functionality typical of living materials.”
Lasers are devices that amplify light to produce a special form of light. The self-assembling lasers in the team’s experiment consisted of microparticles dispersed in a liquid with high ‘gain’ – the ability to amplify light. Once enough of these microparticles collect together, they can harness external energy to ‘lase’ – produce laser light.
An external laser was used to heat up a ‘Janus’ particle (a particle coated on one side with light-absorbing material), around which the microparticles gathered. The lasing created by these microparticle clusters could be turned on and off by changing the intensity of the external laser, which in turn controlled the size and density of the cluster.
The team also showed how the lasing cluster could be transferred in space by heating different Janus particles, demonstrating the adaptability of the system. Janus particles can also collaborate, creating clusters that have properties beyond the simple adding of two clusters, such as changing their shape and boosting their lasing power.
Co-lead author Dr Giorgio Volpe, from the Department of Chemistry at UCL, said: “Nowadays, lasers are used as a matter of course in medicine, telecommunications, and also in industrial production. Embodying lasers with life-like properties will enable the development of robust, autonomous, and durable next-generation materials and devices for sensing applications, non-conventional computing, novel light sources and displays.”
Next, the team will study how to improve the lasers’ autonomous behaviour to render them even more life-like. A first application of the technology could be for next-generation electronic inks for smart displays.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hayley Dunning
Imperial College London
Office: 020-759-42412
Copyright © Imperial College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








