Home > Press > An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy
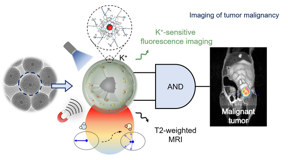 |
| A K+ sensitive dual-mode nanoprobe with superior magnetic resonance contrast effect and K+-specific fluorescence imaging performance is developed for non-invasive tumor imaging and malignancy identification via a cascaded ‘AND’ logic operation. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Tumor malignancy identification plays an essential role in clinical management of cancer. Currently, biopsy is the gold standard for malignancy identification in most tumor cases, it is, however, invasive that can cause great discomfort to patients, and potentially increase the risk of distant metastases due to the complex sampling process. With the development of molecular imaging probes, non-invasive medical imaging approaches, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), fluorescence imaging (FI), computed tomography, and ultrasound, etc., have been used for non-invasive tumor diagnosis. Nevertheless, majority of imaging strategies are often dependent on imaging probes that lack specificity for identification of tumor malignancy.
An artificial intelligence probe help see tumor malignancy
Beijing, China | Posted on July 1st, 2022Considering that necrotic cell death and overexpressed potassium ions (K+) channels are major hallmarks of malignant tumors, but not for benign ones, the extracellular K+ concentration is significantly elevated in the malignant tumor microenvironment compared with that of benign tissue. Based on this, a new research led by Prof. Daishun Ling from Shanghai Jiao Tong University reported a K+-sensitive dual-mode imaging probe (KDMN) to realize real-time tumor imaging while identifying the malignancy.
The KDMN consists of optical K+ indicators embedded in magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticle, which is subsequently coated with a K+-selective membrane that exclusively permits the passage of K+ while excluding other cations. The KDMNs afford superior MR contrast effect and K+-specific FI performance. Moreover, KDMN-enhanced MRI confers attenuated signals at the tumor sites for effective tumor detection. Meanwhile, KDMN-based K+-sensitive FI provides a significant difference in fluorescence signals between malignant tumors and benign ones because there is an elevated extracellular K+ concentration in the malignant tumor microenvironment. Notably, the integration of KDMN-based MRI and FI via cascaded logic circuit has successfully achieved self-confirmation of dual-mode imaging results, thus allowing reliable and accurate imaging of tumor malignancy.
The study was recently published in National Science Review. The first author is Dr. Qiyue Wang, and the corresponding authors are Prof. Daishun Ling from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Prof. Fangyuan Li from Zhejiang University. “This is the first demonstration of a K+-sensitive dual-mode imaging probe for MRI/FI-cross-checked diagnosis of tumor malignancy,” Prof. Ling said. “And this ion-sensitive cascaded ‘AND’ logic imaging strategy would pave the way for the development of next-generation imaging probes for highly sensitive and accurate diagnosis of ion dyshomeostasis associated diseases.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Office: 86-10-64015905
Expert Contact
Daishun Ling
Frontiers Science Center for Transformative Molecules, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, National Center for Translational Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








