Home > Press > Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities
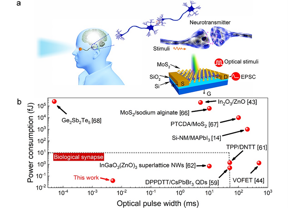 |
| Figure 1 (a) Schematic diagram of visual perception and information transmission in human brain and corresponding artifical MoS2 synaptic device; (b) Comparison of single optical pulse width and power consumption among some synaptic devices. CREDIT OEA |
Abstract:
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2022.210069 discusses how photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities.
Photonic synapses with low power consumption and high sensitivity are expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities
Shannon, Ireland | Posted on July 1st, 2022Neuromorphic photonics/electronics is the future of ultralow energy intelligent computing and artificial intelligence (AI). In recent years, inspired by the human brain, artificial neuromorphic devices have attracted extensive attention, especially in simulating visual perception and memory storage. Because of its advantages of high bandwidth, high interference immunity, ultrafast signal transmission and lower energy consumption, neuromorphic photonic devices are expected to realize real-time response to input data. In addition, photonic synapses can realize non-contact writing strategy, which contributes to the development of wireless communication. The use of low-dimensional materials provides an opportunity to develop complex brain-like systems and low-power memory logic computers. For example, large-scale, uniform and reproducible transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) show great potential for miniaturization and low-power biomimetic device applications due to their excellent charge-trapping properties and compatibility with traditional CMOS processes. The von Neumann architecture with discrete memory and processor leads to high power consumption and low efficiency of traditional computing. Therefore, the sensor-memory fusion or sensor-memory- processor integration neuromorphic architecture system can meet the increasingly developing demands of big data and AI for low power consumption and high performance devices. Artificial synaptic devices are the most important components of neuromorphic systems. The performance evaluation of synaptic devices will help to further apply them to more complex artificial neural networks (ANN).
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)-grown TMDs inevitably introduce defects or impurities, showed a persistent photoconductivity (PPC) effect. TMDs photonic synapses integrating synaptic properties and optical detection capabilities show great advantages in neuromorphic systems for low-power visual information perception and processing as well as brain memory.
The research Group of Optical Detection and Sensing (GODS) have reported a three-terminal photonic synapse based on the large-area, uniform multilayer MoS2 films. The reported device realized ultrashort optical pulse detection within 5 μs and ultralow power consumption about 40 aJ, which means its performance is much better than the current reported properties of photonic synapses. Moreover, it is several orders of magnitude lower than the corresponding parameters of biological synapses, indicating that the reported photonic synapse can be further used for more complex ANN. The photoconductivity of MoS2 channel grown by CVD is regulated by photostimulation signal, which enables the device to simulate short-term synaptic plasticity (STP), long-term synaptic plasticity (LTP), paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) and other synaptic properties. Therefore, the reported photonic synapse can simulate human visual perception, and the detection wavelength can be extended to near infrared light. As the most important system of human learning, visual perception system can receive 80% of learning information from the outside. With the continuous development of AI, there is an urgent need for low-power and high sensitivity visual perception system that can effectively receive external information. In addition, with the assistant of gate voltage, this photonic synapse can simulate the classical Pavlovian conditioning and the regulation of different emotions on memory ability. For example, positive emotions enhance memory ability and negative emotions weaken memory ability. Furthermore, a significant contrast in the strength of STP and LTP based on the reported photonic synapse suggests that it can preprocess the input light signal. These results indicate that the photo-stimulation and backgate control can effectively regulate the conductivity of MoS2 channel layer by adjusting carrier trapping/detrapping processes. Moreover, the photonic synapse presented in this paper is expected to integrate sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities, which can be used for real-time image detection and in-situ storage, and also provides the possibility to break the von Neumann bottleneck.
# # # # # #
Group of Optical Detection and Sensing (GODS) was established in 2019. It is a research group focusing on compound semiconductors, lasers, photodetectors, and optical sensors. GODS has established a well-equipped laboratory with research facilities such as Molecular Beam Epitaxy system, IR detector test system, etc. GODS is leading several research projects funded by NSFC and National Key R&D Programmes. GODS have published more than 100 research articles in Nature Electronics, Light: Science and Applications, Advanced Materials and other international well-known high-level journals with the total citations beyond 8000.
https://uestcgods.com/
Jiang Wu obtained his Ph.D. from the University of Arkansas Fayetteville in 2011. After his Ph.D., he joined UESTC as associate professor and later professor. He joined University College London as a research associate in 2012 and then lecturer in the Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering at UCL from 2015 to 2018. He is now a professor at UESTC. His research interests include optoelectronic applications of semiconductor heterostructures. He is a Fellow of the Higher Education Academy and Senior Member of IEEE.
####
About Compuscript Ltd
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 9.682 (Journals Citation Reports for IF 2020). Since its launch in March 2018, OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases over the time and expanded its Editorial Board to 36 members from 17 countries and regions (average h-index 49).
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Conor Lovett
Compuscript Ltd
Office: 353-614-75205
Copyright © Compuscript Ltd
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








