Home > Press > From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en
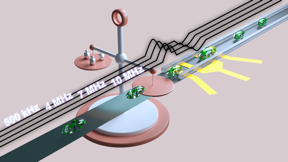 |
| Precise total assessment of the cells with impedance signals. CREDIT Tao Tang, Yaxiaer Yalikun |
Abstract:
Having a good eye for detail is an essential skill for many professions. In particular, biologists use special techniques and advanced technology to analyze individual cells with unprecedented precision. Impedance cytometry is one experimental method that can reveal specific characteristics of living single cells. This technique requires electrical penetration, in which high-frequency current can freely pass through the cell membrane, without damaging the cell. Now, researchers from Japan have determined optimal conditions to perform impedance cytometry. Their work may lead to rapid assessment of cells during culture in biological experiments.
From outside to inside: A rapid and precise total assessment method for cells: Researchers at Nara Institute of Science and Technology show that using four frequencies of applied voltage can improve the measurement of cell size and shape during impedance cytometry, enabling to en
Ikoma, Japan | Posted on June 24th, 2022An improved method for measuring the morphology and biomass of single cells using impedance cytometry has been introduced in a recently published study in Microsystems & Nanoengineering. Impedance cytometry involves applying high-frequency voltages to electrodes to measure complex impedance, which can provide information about the shape and effective volume of the cell. In the study, researchers led by Nara Institute of Science and Technology used different phases of voltage signals at four frequencies. They showed that applied voltages with frequencies of around 7 MHz are able to pass through the membrane of Euglena gracilis cells. Higher frequencies can monitor changes in biomass, while lower frequencies can track volume changes.
When a high-frequency electrical field penetrates the cell membrane, the uneven intracellular distribution tilts the impedance pulses to the left or right, which has been verified in simulation and experiments. “Ultimately, our method for determining the conductivity of the cell membrane relies on the degree of tilt caused by the electrical pulses,” says author Yoichiroh Hosokawa. The team also performed calibration studies using beads to better understand the underlying physical mechanisms of this effect.
“This research enables the easy determination of the electrical penetration of a cell membrane, and the proposed platform is applicable to multiparameter assessment of the organism’s state during cultivation,” says senior author Yaxiaer Yalikun. This platform may be easily integrated into microfluidic systems for the scalable monitoring of biological experiments.
The need for efficient and highly accurate analysis of living single cells may be met by this new impedance cytometry method developed by the research team led by Nara Institute of Science and Technology. Future applications could be extended to cells in mammals to monitor specific membrane changes in fields such as oncogenesis and cell aging.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Takahito Shikano
Nara Institute of Science and Technology
Copyright © Nara Institute of Science and Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Information about the Bio-Process Engineering Laboratory can be found at the following website:
Information about the Bio-Process Engineering Laboratory can be found at the following website:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








