Home > Press > Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus’s ability to bind to host cells
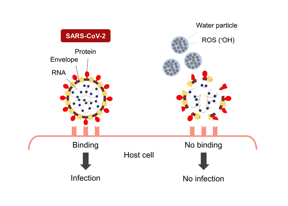 |
| When the envelope, protein, and RNA of SARS-CoV-2 are damaged by nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles, the virus is unable to bind to host cells. CREDIT Osaka Metropolitan University |
Abstract:
Current disinfection strategies have major drawbacks, which is why the World Health Organization does not advise routine spraying or fogging of biocidal agents, or UV light sterilization, in occupied areas. One possible alternative is nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles generated by an electrospray device developed by Panasonic Corporation. The water particles contain reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage lipid, protein, and DNA and are reported to disinfect several bacterial and viral species.
Disinfectant mechanism of nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles on SARS-CoV-2: Nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2 envelope, protein, and RNA, thereby impairing the virus’s ability to bind to host cells
Osaka, Japan | Posted on June 17th, 2022In their previous research, Associate Professor Yasugi’s team showed that nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2, but the mechanism remained a mystery. Their new paper published in the Journal of Nanoparticle Research describes the damage they observed when SARS-CoV-2 was exposed to the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles.
The researchers showed the atomized water particles decreased the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 to cells while observing the damage to the virus. “We observed that the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles damaged the viral envelope, protein, and RNA, making them unable to bind to host cells,” Associate Professor Yasugi explained. “The phenomena we observed are considered the main mechanism by which the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2.We found that the target of the water particles is not the specific viral specific structure or specific proteins. Because the water particles impact viral envelope, protein, and RNA, they may disinfect other enveloped viral species as well.”
While this proof of concept demonstrates how the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2, the full extent of their application remains to be seen. “We don’t know the precise factor destroying SARS-CoV-2; ROS in the particles may be that factor because ROS damage lipid, protein, and DNA/RNA through their oxidation. Furthermore, our studies showed the water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces under closed experimental conditions. But the efficacy of the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles can change depending on the humidity, temperature, and other environmental factors; for this method to be practical, it would have to work in numerous environments,” Associate Professor Yasugi concluded. “Our future studies will focus on the ROS mechanism of action and test if the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles are effective against airborne SARS-CoV-2.”
####
About Osaka Metropolitan University
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.upc-osaka.ac.jp/new-univ/en-research/research/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jens Herzog
Osaka Metropolitan University
Copyright © Osaka Metropolitan University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








