Home > Press > Observation of fractional exclusion statistics in quantum critical matter
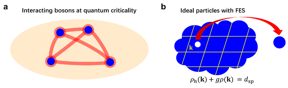 |
| Figure 1. Quantum critical matter and fractional exclusion statistics. (a) Interacting bosons at quantum criticality. (b) Ideal particles with FES. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
A quantum system consisting of a large number of microscopic particles obeys statistical laws at the macroscopic level. In nature, there are two kinds of microscopic quantum particles. One is boson satisfying the Bose-Einstein statistics, and the other is fermion satisfying the Fermi-Dirac statistics. However, for interacting quantum systems, such two types of statistics are not the only forms of quantum statistics. For instance, anyonic statistics can emerge in two-dimensional (2D) electrons. In 1991, Nobel Physics Prize winner F. D. M. Haldane proposed a novel concept of fractional exclusion statistics (FES), which is a generalized statistical distribution, with the Bose and Fermi distributions being its two limiting cases. In 1994, physicist Yongshi Wu and others studied the thermodynamic properties of systems satisfying FES. Subsequently, the theory of the FES has been used to perform theoretical studies on the fractional Hall effect, quantum gases, spin models, anyons and many other quantum many-body problems. However, observation of the FES in realistic experiments still remains challenging and sparse.
Observation of fractional exclusion statistics in quantum critical matter
Beijing, China | Posted on May 27th, 2022One-dimensional Bose gases with repulsive interaction has become an important platform for the experimental study of quantum many-body physics in recent years. Such gases have been theoretically shown to satisfy mutual FES in quasi-momentum space. However, the couplings between different quasi-momenta make it very hard to obtain a direct relation between measurable physical quantities and the statistics parameter. Recently, Xibo Zhang and his coworkers found that for 1D and 2D quantum Bose gases in the quantum critical regime, the couplings between quasi-momenta become rather local, and a simple, non-mutual FES emerges. They established a simple correspondence between the interaction strength and the statistics parameter. Based on theoretical computations, numerical quantum Monte Carlo simulations, and experimental measurements, the researchers confirmed that the critical entropy per particle and other thermodynamical quantities are determined by those of non-interacting particles obeying the FES.
This study not only provides a simple physical picture with theoretical, numerical, and experimental evidences for the emergence of the FES in interacting quantum systems, but also provides new prospects and a novel method for understanding the critical behavior of more complex quantum many-body systems, such as quantum gases with SU(N) symmetries, etc.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Office: 86-10-64015905
Expert Contact
Xibo Zhang
International Center for Quantum Materials (ICQM), School of Physics, Peking University
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








