Home > Press > Injectable stem cell assembly for cartilage regeneration
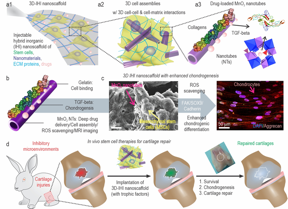 |
| a) A schematic illustration of 3D TGFβ-BMSC-IHI nanoscaffold. b) The schematic illustration of gelatin-coated and TGF-β3-loaded MnO2 NTs. c) The FESEM image indicated that most of the BMSCs form contacts with other cells and the 1D fibril-like structures, which was similar to the structures of natural tissues. d) By remodeling the oxidative microenvironment, enhancing cell viability, and chondrogenesis of transplanted cells, cartilage regeneration could be finally achieved. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
This study led by Prof. Qiuyu Zhang (Northwestern Polytechnical University), Prof. Ki-Bum Lee (Rutgers University), and Prof. Liang Kong (School of Stomatology, The Fourth Military Medical University). They established an injectable hybrid inorganic (IHI) nanoscaffold-templated stem cell assembly and applied it to the regeneration of critically-sized cartilage defects.
Injectable stem cell assembly for cartilage regeneration
Beijing, China | Posted on April 15th, 2022Cartilage injuries are often devastating and most of them have no cures due to the intrinsically low regeneration capacity of cartilage tissues. The rise of 3D stem cell culture systems has led to breakthroughs in developmental biology, disease modeling, and regenerative medicine. For example, stem cells, once transplanted successfully, could initially secret trophic factors for reducing inflammation at sites of cartilage injuries and then differentiate into cartilage cells (e.g., chondrocytes) for functional restoration. Nevertheless, there are critical barriers remaining to be overcome before the therapeutic potential of stem cell therapies can be realized. The limited control over the chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in vivo has often resulted in compromised regenerative outcomes. Moreover, due to the prevalence of oxidative stress and inflammation in the microenvironment of injury sites, stem cells frequently undergo apoptosis after injection.
To address these challenges, they demonstrated the development of a 3D IHI nanoscaffold-templated stem cell assembly system for advanced 3D stem cell culture and implantation. 3D-IHI nanoscaffold rapidly assembles stem cells into injectable tissue constructs through tailored 3D cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, deeply and homogeneously delivers chondrogenic proteins in the assembled 3D culture systems, and controllably induces chondrogenesis through nanotopographical effects. Once implanted in vivo in a rabbit cartilage injury model, 3D-IHI nanoscaffold effectively modulates dynamic microenvironment after cartilage injury through the integration of the aforementioned regenerative cues, and simultaneously scavenges reactive oxygen species using a manganese dioxide-based composition. In this way, accelerated repair of cartilage defects with rapid tissue reconstruction and functional recovery is realized both in the short term and long term. Given the excellent versatility and therapeutic outcome of 3D-IHI nanoscaffold-based cartilage regeneration, it may provide promising means to advance a variety of tissue engineering applications. The first authors are Dr. Shenqiang Wang, Dr. Letao Yang, and Prof. Bolei Cai.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Office: 86-10-64015905
Expert Contact
Prof. Qiuyu Zhang
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








