Home > Press > Development of low-power and high-efficiency artificial sensory neurons: 3T-OTS device to simulate the efficient information processing method of the human brain. A green light for the development of sensor-AI combined next-generation artificial intelligence “to be used in life a
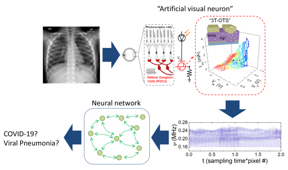 |
| Distinguishing COVID-19 infection through image learning of chest X-rays CREDIT Korea Institute of Science and Technology |
Abstract:
Currently, AI services spread rapidly in daily life and in all industries. These services are enabled by connecting AI centers and terminals such as mobile devices, PCs, etc. This method, however, increases the burden on the environment by consuming a lot of power not only to drive the AI system but also to transmit data. In times of war or disasters, it may become useless due to the power collapse and network failures, the consequences of which may be even more serious if it is an AI service in the life and safety field. As a next-generation artificial intelligence technology that can overcome these weaknesses, low-power and high-efficiency 'in-sensor computing' technology that mimics the information processing mechanism of the human nervous system is drawing attention
Development of low-power and high-efficiency artificial sensory neurons: 3T-OTS device to simulate the efficient information processing method of the human brain. A green light for the development of sensor-AI combined next-generation artificial intelligence “to be used in life a
Yeongi-gun, South Korea | Posted on April 8th, 2022The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, President Seok-Jin Yoon) announced that its team led by Dr. Suyoun Lee (Center for Neuromorphic Engineering) has succeeded in developing ‘artificial sensory neurons’ that will be the key to the practical use of in-sensor computing. Neurons refine vast external stimuli (received by sensory organs such as eyes, nose, mouth, ears, and skin) into information in the form of spikes; and therefore, play an important role in enabling the brain to quickly integrate and perform complex tasks such as cognition, learning, reasoning, prediction, and judgment with little energy.
The Ovonic threshold switch (OTS) is a two-terminal switching device that maintains a high resistance state (10-100 MΩ) below the switching voltage, and exhibits a sharp decrease in resistance above the switching voltage. In a precedent study, the team developed an artificial neuron device that mimics the action of neurons (integrate-and-fire) that generates a spike signal when the input signal exceeds a specific intensity.
This study, furthermore, introduces a 3-terminal Ovonic Threshold Switch (3T-OTS) device that can control the switching voltage in order to simulate the behavior of neurons and quickly find and abstract patterns among vast amounts of data input to sensory organs. By connecting a sensor to the third electrode of the 3T-OTS device, which converts external stimuli into voltage, it was possible to realize a sensory neuron device that changes the spike patterns according to the external stimuli.
The research team succeeded in realizing an artificial visual neuron device that mimics the information processing method of human sensory organs, by combining a 3T-OTS and a photodiode. In addition, by connecting an artificial visual neuron device with an artificial neural network that mimics the visual center of the brain, the team could distinguish COVID-19 infections from viral pneumonia with an accuracy of about 86.5% through image learning of chest X-rays.
Dr Suyoun Lee, Director of the KIST Center for Neuromorphic Engineering, said, “This artificial sensory neuron device is a platform technology that can implement various sensory neuron devices such as sight and touch, by connecting with existing sensors. It is a crucial building block for in-sensor computing technology.” He also explained the significance of the research that “will make a great contribution to solving various social problems related to life and safety, such as, developing a medical imaging diagnostic system that can diagnose simultaneously with examinations, predicting acute heart disease through time-series pattern analysis of pulse and blood pressure, and realizing extrasensory ability to detect vibrations outside the audible frequency to prevent building collapse accidents, earthquakes, tsunamis, etc.”.
####
About National Research Council of Science & Technology
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute to establish a national development strategy based on science and technology and disseminate various industrial technologies to develop major industries. KIST is now raising Korean science and technology status through world-leading innovative research and development.
This work was supported by the KIST Institutional Program, as well as by the Future Semiconductor New Device Source Technology Development Program and the Next Generation Intelligence Semiconductor Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT(Minister: Lim, Hyesook). The research results were published in the latest issue of the ‘Nano Letters' (IF: 11.189, top 9.062% of the JCR field), an authoritative journal in the fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Young Mi Kim
National Research Council of Science & Technology
Office: 82-442-877-376
Expert Contacts
Dr. Lee, Suyoun
Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-6679
Lee, Yeeun (PR Department)
Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Office: +82-2-958-6929
Copyright © National Research Council of Science & Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Artificial Intelligence
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








