Home > Press > NGI advances graphene spintronics as 1D contacts improve mobility in nano-scale devices
 |
Abstract:
Researchers at The University of Manchester may have cleared a significant hurdle on the path to quantum computing, demonstrating step-change improvements in the spin transport characteristics of nanoscale graphene-based electronic devices.
NGI advances graphene spintronics as 1D contacts improve mobility in nano-scale devices
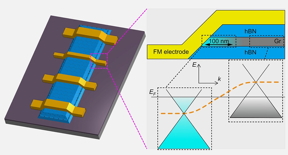
Manchester, UK | Posted on February 11th, 2022The team - comprising researchers from the National Graphene Institute (NGI) led by Dr Ivan Vera Marun, alongside collaborators from Japan and including students internationally funded by Ecuador and Mexico - used monolayer graphene encapsulated by another 2D material (hexagonal boron nitride) in a so-called van der Waals heterostructure with one-dimensional contacts (main picture, above). This architecture was observed to deliver an extremely high-quality graphene channel, reducing the interference or electronic ‘doping’ by traditional 2D tunnel contacts.
‘Spintronic’ devices, as they are known, may offer higher energy efficiency and lower dissipation compared to conventional electronics, which rely on charge currents. In principle, phones and tablets operating with spin-based transistors and memories could be greatly improved in speed and storage capacity, exceeding Moore’s Law.
As published in Nano Letters, the Manchester team measured electron mobility up to 130,000cm2/Vs at low temperatures (20K or -253oC). For purposes of comparison, the only previously published efforts to fabricate a device with 1D contacts achieved mobility below 30,000cm2/Vs, and the 130k figure measured at the NGI is higher than recorded for any other previous graphene channel where spin transport was demonstrated.
The researchers also recorded spin diffusion lengths approaching 20μm. Where longer is better, most typical conducting materials (metals and semiconductors) have spin diffusion lengths <1μm. The value of spin diffusion length observed here is comparable to the best graphene spintronic devices demonstrated to date.
Lead author of the study Victor Guarochico said: “Our work is a contribution to the field of graphene spintronics. We have achieved the largest carrier mobility yet regarding spintronic devices based on graphene. Moreover, the spin information is conserved over distances comparable with the best reported in the literature. These aspects open up the possibility to explore logic architectures using lateral spintronic elements where long-distance spin transport is needed.”
Co-author Chris Anderson added: “This research work has provided exciting evidence for a significant and novel approach to controlling spin transport in graphene channels, thereby paving the way towards devices possessing comparable features to advanced contemporary charge-based devices. Building on this work, bilayer graphene devices boasting 1D contacts are now being characterised, where the presence of an electrostatically tuneable bandgap enables an additional dimension to spin transport control.”
Discover more about our capabilities in graphene and 2D material research at the National Graphene Institute website.
Advanced materials is one of The University of Manchester’s research beacons - examples of pioneering discoveries, interdisciplinary collaboration and cross-sector partnerships that are tackling some of the biggest questions facing the planet. #ResearchBeacons
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ben Robinson
University of Manchester
Office: 01-612-750-134
Copyright © University of Manchester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








