Home > Press > Scientists enhance energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating
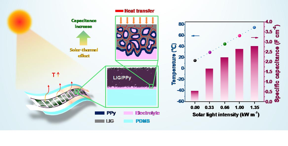 |
| Schematic diagram of fabricating process for the solar-thermal MSC and their energy storage performance under different light intensities CREDIT LI Nian |
Abstract:
Prof. WANG Zhenyang's research group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has enhanced the energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating. Related research results were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
Scientists enhance energy storage capacity of graphene supercapacitors via solar heating
Hefei, China | Posted on January 28th, 2022In low temperature environments, the hindered diffusion of electrolyte ions seriously restricts the electrochemical performance of supercapacitors. Electrode materials with solar-thermal properties are expected to provide a new strategy to solve this problem. However, it remains a challenge to develop electrode materials with both excellent solar-thermal properties and high energy storage capacity.
In this research, the researchers prepared graphene films with three-dimensional porous structures using laser-induction technology. They composited the polypyrrole uniformly composited into the graphene network by pulse electrodeposition. Graphene/polypyrrole composite electrodes were obtained and a new type of solar-thermally enhanced supercapacitor was thus constructed.
This supercapacitor has many advantages. When the temperature dropped to -30 centigrade, the electrochemical performance of the supercapacitor, which is normally severely degraded, could be enhanced rapidly to room temperature under solar irradiation at light intensities of 1.0 kW m-2. Meanwhile, at room temperature (15°C), the surface temperature of the devices increased by 45°C under solar irradiation at light intensities of 1.0 kW m-2.
"After the temperature of electrodes was raised, the optimized pore structure and the increased electrolyte ion diffusion rate increased the energy storage capacity by 4.8 times. In addition, since the solid electrolyte was well protected, the capacitance retention rate of the supercapacitor was still as high as 85.8% after 10,000 times of charging and discharging," said Dr. LI Nian, a member of the team.
This work provided new solutions for solving the low temperature problem of supercapacitors and developing high energy density devices and was supported by the National Key R&D Project of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Anhui Provincial Science and Technology Major Project, and the Anhui Provincial Key R&D Program.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Weiwei Zhao
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Office: 86-551-655-91206
Copyright © Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








