Home > Press > Studied for clean energy, carbon nanotubes find new potential in anticancer drug delivery: Short carbon nanotubes in liposome membranes help fuse the liposomes and cancer cells to directly deliver a cancer-killing drug
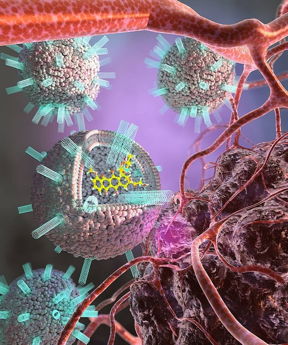 |
| Liposomes studded with carbon nanotubes and carrying a chemotherapy drug dock to the surface of a cancer cell. This causes the liposome to fuse to the cancer cell and deliver the drug, killing the cell. CREDIT Image courtesy of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Image created by EllaMaru Studios. |
Abstract:
The Science
Fundamental science often finds applications beyond its original focus. Previously, scientists found applications for small diameter carbon nanotube porins in energy technology. Nanotube porins are tubes with walls just molecules thick that act as pores through the walls of a thin membrane of liposomes, a type of tiny synthetic particle. Scientists have now assembled these nanotubes in a new way to deliver a cancer drug. The key is that the nanotubes pull the liposomes and the cancer cells together, allowing the membranes of the liposome and cancer to mix. This fusion process allows the drug to freely pass from the liposome to the cell. This results in very effective delivery of the anticancer drug doxorubicin, killing up to 90 percent of diseased cells.
Studied for clean energy, carbon nanotubes find new potential in anticancer drug delivery: Short carbon nanotubes in liposome membranes help fuse the liposomes and cancer cells to directly deliver a cancer-killing drug
Washington, DC | Posted on January 28th, 2022The Impact
This new pathway to deliver a drug directly into a cell interior addresses a long-standing challenge for medicine. It provides a new platform for understanding how to precisely deliver a wide range of drugs to individual cells. This understanding will potentially enhance the arsenal of innovative drug carriers for treatment of difficult to cure diseases. Another potential application includes more efficient methods for administering vaccines.
Summary
Carbon nanotube pores that create and maintain water “wires” could allow for rapid transport of protons in next-generation, artificial, proton-conducting membranes. These membranes could lead to applications such as more efficient fuel cells for powering cars and homes. Scientists have now used reconfigured versions of these same carbon nanotubes to directly introduce the anticancer drug doxorubicin from spherical sacs of phospholipid molecules (liposomes) through the cell plasma membrane into its interior. Chemotherapy is an effective treatment for many cancer patients but delivering these drugs into unhealthy cells is still quite difficult. Doctors have used liposomes to deliver therapeutic drugs to diseased cells for some time. However, this process usually follows an inefficient delivery pathway, and the drugs are often destroyed before they get to the cells. This pathway is bypassed when small diameter, carbon nanotube porins are incorporated into liposomes full of the anticancer drug. These porins allow fusion of liposome and cell membranes, permitting direct delivery of the drug. Computational simulations revealed that tiny dimers of carbon nanotubes embedded in the exterior of the liposome membrane first tether the liposome and cell membranes together very closely. Mixing of the membranes induced by such proximity causes the cells and liposomes to blend. This leads to direct delivery of the drug, killing most of the cancer cells.
Funding
This research was primarily supported by the Department of Energy Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences and the Laboratory Directed Research and Development program at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Analysis of kinetics was supported by the National Science Foundation and computational work was supported by the Max Planck Society.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Church
DOE/US Department of Energy
Office: 2028416299
Copyright © DOE/US Department of Energy
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








