Home > Press > A single molecule makes a big splash in the understanding of the two types of water
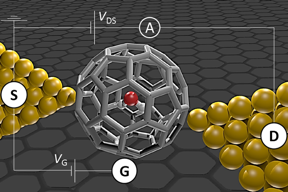 |
| A collaborative team led by researchers from Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo uses a single water molecule in a C60 cage to probe quantum mechanics CREDIT Institute of Industrial Science, the University of Tokyo |
Abstract:
It plays a fundamental role in human existence and is a major component of our universe, yet there are still things we don’t understand about water. To address the knowledge gaps, a collaborative team of Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, Kyoto University, and Tohoku University investigated electron transport through a single water molecule in a C60 cage. Their findings are published in Nano Letters.
A single molecule makes a big splash in the understanding of the two types of water
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on January 7th, 2022Simple systems are often the best starting point for determining complex information. A single water molecule is one such system. Made up of just three atoms, it provides an excellent model for establishing quantum mechanical information.
Introducing a water molecule into a C60 cage—a soccer ball-shaped molecule made entirely of carbon atoms—gives and is an excellent way of isolating water for investigation. The researchers achieved this using “molecular surgery”, which involves opening the cage, injecting water, and closing the cage again.
was then used as a single molecule transistor (SMT) by mounting one molecule in the very small gap—less than 1 nm—between two gold electrodes. Because the electric current then passes through the isolated molecule only, the electron transport can be studied with high specificity.
A conductance map, also known as a “Coulomb stability diagram”, was generated for the SMT. It showed multiple tunneling-induced excited states for the water molecule. In contrast, the Coulomb stability diagram of an empty C60 cage SMT showed only two excited states.
“Because it contains two hydrogen atoms, water has two different nuclear spin states: ortho- and para-water. In ortho-water the hydrogen nuclear spins are in the same direction, while in para-water they are opposite to one another,” explains study lead author Shaoqing Du. “Understanding the transition between these two types of water is an important area of research.”
The researchers measured tunneling spectra for the system and, by comparing the findings with theoretical calculations, were able to attribute the measured conductance peaks to rotational and vibrational excitations of the water molecule. They also investigated using terahertz spectroscopy and the results agreed with the tunneling spectroscopy data.
Both techniques showed quantum rotational excitations of ortho- and para-water simultaneously. This demonstrates that the single water molecule transitioned between the two nuclear isomers (ortho- and para-water) within the timeframe of the experiment, which was approximately one minute.
“Our findings make an important contribution to the understanding of ortho-para fluctuation in water molecules,” says study corresponding author Kazuhiko Hirakawa. “Because water plays such an important role in chemistry and biology, and even in understanding our universe, we expect our findings to have a wide-ranging impact.”
####
About Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo is one of the largest university-attached research institutes in Japan.
More than 120 research laboratories, each headed by a faculty member, comprise IIS, with more than 1,200 members including approximately 400 staff and 800 students actively engaged in education and research. Our activities cover almost all the areas of engineering disciplines. Since its foundation in 1949, IIS has worked to bridge the huge gaps that exist between academic disciplines and realworld applications.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kazuhiko Hirakawa
Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
Office: 81-3-5452-6260
Copyright © Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








