Home > Press > Cancer cells use ‘tiny tentacles’ to suppress the immune system: With the power of nanotechnology, investigators have discovered that cancer cells strengthen by forming nanotubes that they use to suck mitochondria out of immune cells
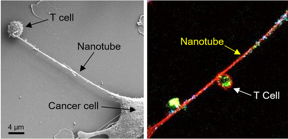 |
| Left: Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) image shows the formation of a nanotube between a breast cancer cell and an immune cell. Right: Confocal microscopy image shows mitochondria (labeled with green fluorescence dye) traveling from a T cell to a cancer cell through the intercellular nanotube. DNA in the mitochondria was labeled with blue dye. CREDIT Nature Nanotechnology https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-01000-4 |
Abstract:
To grow and spread, cancer cells must evade the immune system. Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and MIT used the power of nanotechnology to discover a new way that cancer can disarm its would-be cellular attackers by extending out nanoscale tentacles that can reach into an immune cell and pull out its powerpack. Slurping out the immune cell’s mitochondria powers up the cancer cell and depletes the immune cell. The new findings, published in Nature Nanotechnology, could lead to new targets for developing the next generation of immunotherapy against cancer.
Cancer cells use ‘tiny tentacles’ to suppress the immune system: With the power of nanotechnology, investigators have discovered that cancer cells strengthen by forming nanotubes that they use to suck mitochondria out of immune cells
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 19th, 2021“Cancer kills when the immune system is suppressed and cancer cells are able to metastasize, and it appears that nanotubes can help them do both,” said corresponding author Shiladitya Sengupta, PhD, co-director of the Brigham’s Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “This is a completely new mechanism by which cancer cells evade the immune system and it gives us a new target to go after.”
To investigate how cancer cells and immune cells interact at the nanoscale level, Sengupta and colleagues set up experiments in which they co-cultured breast cancer cells and immune cells, such as T cells. Using field-emission scanning electron microscopy, they caught a glimpse of something unusual: Cancer cells and immune cells appeared to be physically connected by tiny tendrils, with widths mostly in the 100-1000 nanometer range. (For comparison, a human hair is approximately 80,000 to 100,000 nanometers). In some cases, the nanotubes came together to form thicker tubes. The team then stained mitochondria — which provide energy for cells — from the T cells with a fluorescent dye and watched as bright green mitochondria were pulled out of the immune cells, through the nanotubes, and into the cancer cells.
“By carefully preserving the cell culture condition and observing intracellular structures, we saw these delicate nanotubes and they were stealing the immune cells’ energy source,” said co-corresponding author Hae Lin Jang, PhD, a principal investigator in the Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “It was very exciting because this kind of behavior had never been observed before in cancer cells. This was a tough project as the nanotubes are fragile and we had to handle the cells very gently to not break them.”
The researchers then looked to see what would happen if they prevented the cancer cells from hijacking mitochondria. When they injected an inhibitor of nanotube formation into mouse models used for studying lung cancer and breast cancer, they saw a significant reduction in tumor growth.
“One of the goals in cancer immunotherapy is to find combinations of therapies that can improve outcomes,” said lead author Tanmoy Saha, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the Center for Engineered Therapeutics. “Based on our observations, there is evidence that an inhibitor of nanotube formation could be combined with cancer immunotherapies and tested to see if it can improve outcomes for patients.”
Disclosures: Sengupta is a co-founder and owns equity in Vyome Therapeutics, Akamara Therapeutics and Invictus Oncology, and receives fees from Famygen and Advamedica. Jang is a founder and owns equity in Curer. A full list of other author disclosures is available online.
Funding: This work is supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (NIH AR073135_HLJ, CA236702_SS_HLJ, CA214411_SS and CA229772_SS_Co-I), American Lung Association Discovery Grant (LCD-618834_SS) and Department of Defense (DoD PC180355_HLJ and CA201065_HLJ). This work was performed in part at the Center for Nanoscale Systems (CNS), Harvard University, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure Network (NNCI), supported by the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Serena Bronda
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Office: 617-525-6373
Copyright © Brigham and Women’s Hospital
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








