Home > Press > MXene-GaN van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions for high performance photodetection
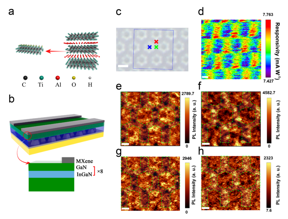 |
| a, Schematic illustration of the synthesis and structure of Ti3C2Tx MXene. b, Schematic diagram of the proposed PD prepared on the patterned sapphire substrate. c, high magnification (scale bar: 3 μm) optical images of the proposed PD. Inside the blue box is the finer area responsivity and photoluminescence mapping region. d, The responsivity mapping inside the blue box when the proposed PD at +5V bias (scale bar: 1 μm). The photoluminescence intensity mapping of the blue box region in Fig. 4b at the extracted Fabry-Pérot interference wavelengths of e 524.2 nm (trough), f 520.7 nm (peak), g 517.3 nm (trough) and h 513.1 nm (peak). The scale bar is 1 μm. CREDIT by Lingzhi Luo, Yixuan Huang, Keming Cheng, Abdullah Alhassan, Mahdi Alqahtani, Libin Tang, Zhiming Wang, Jiang Wu |
Abstract:
The application of Internet of Things (IoT) has sparked intense interest of photodetectors (PD) as they are widely used in sensing, detection, data transport and processing. The coming 5G enabled IoT (5G-IoT) will require new performance criteria such as massive connectivity, ultra-low latency, ultra-reliable for huge number of IoT devices. To meet these demands, metal-semiconductor-metal (MSM) photodetectors have received much attention for their high response speed, simple fabrication process and feasibility of integration with field effect transistor (FET) technology. However, the conventional fabrication process will induce chemical disorder and defect states at the metal-semiconductor interfaces, leading to significant dark current and noise. Additionally, opaque metals are usually placed on top of the active light absorption region, which will reflect part of the incident light thus reduce the responsivity of MSM photodetectors.
MXene-GaN van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions for high performance photodetection
Changchun, China | Posted on September 24th, 2021In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Jiang Wu from Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China, and co-workers have demonstrated a high performance MXene-GaN-MXene based multiple quantum well photodetector prepared on patterned sapphire substrate by facile drop casting.
MXene, a new type of two-dimensional (2D) materials discovered in 2011, has many charming properties, such as metallic conductivity, mechanical flexibility, hydrophilia, good transmittance and chemical stability, which enable MXene to be processed in solution at low temperatures and under ambient conditions. Additionally, the widely tunable work function makes MXene a great candidate for ohmic or Schottky contacts with various semiconductor materials. More importantly, 2D materials consist of in-plane covalently bonded atomic layers that interact weakly with each other in the out-of-plane direction. When deposited on bulk semiconductor materials, MXene-semiconductor van der Waals junctions formed at the interface are free of chemical disorder and have less defect states, which could avoid the Fermi level pinning effect and reduce the reverse tunneling currents.
The multiple quantum well photodetector proposed by Jiang et al was grown on the patterned sapphire substrate, which can promote the epitaxial lateral overgrowth (ELOG) mode and consequently reduce the defect density in GaN epilayers and the MXene was employed to replace the conventional metals, Au/Cr. The MXene-GaN-MXene based multiple quantum well photodetector showed significantly improved responsivity, dark current and noise in the blue-green light spectrum range compared with the conventional counterpart, making it a potential candidate for under water optical detection and communication. The improvements were attributed to the low-defect MXene-GaN van der Waals interfaces. More interestingly, thanks to the high quality MXene-GaN van der Waals junctions, which can suppress the dark current and noise hence distinguish minor spatial variation of the photocurrent in the order of nanoamps, the localized light focusing and enhancement by the patterned sapphire substrate were observed.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Copyright © Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Internet-of-Things
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








