Home > Press > Researchers use gold film to enhance quantum sensing with qubits in a 2D material
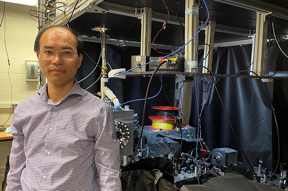 |
| Tongcang Li and his team at Purdue University have developed ultrathin quantum sensors with 2D materials. CREDIT Cheryl Pierce, Purdue University |
Abstract:
As recently as 2019, spin defects known as qubits were discovered in 2D materials (hexagonal boron nitride), which could amplify the field of ultrathin quantum sensing. These scientists hit a snag in their discovery that has unleashed a scientific race to resolve the issues. The sensitivity of spin qubits in hexagonal boron nitride was limited by their low brightness and the low contrast of their magnetic resonance signal. Last month, Nature Physics published an article titled “Quantum sensors go flat,” highlighting the benefits and outlining current shortfalls of this new means of sensing via qubits in 2D materials.
Researchers use gold film to enhance quantum sensing with qubits in a 2D material
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on September 3rd, 2021A team of researchers at Purdue University took on the challenge of overcoming qubit signal shortcomings in their work to develop ultrathin quantum sensors with 2D materials. Their publication in Nano Letters demonstrates that they have solved some of the critical issues and yielded better results through experimentation.
“We used a gold film to increase the brightness of spin qubits by up to 17-fold,” said Tongcang Li, associate professor of physics and astronomy and electrical and computer engineering. “The gold film supports the surface plasmon that can speed up photon emission so we can collect more photons and, hence, more signals. In addition, we improved the contrast of their magnetic resonance signal by a factor of 10 by optimizing the design of a microwave waveguide. As a result, we substantially improved the sensitivity of these spin defects for detecting magnetic field, local temperature and local pressure.”
Funding
Seed grant from Purdue Quantum Science and Engineering Institute, DARPA Nascent Light-Matter Interactions program and the DARPA QUEST program; National Science Foundation (award No. 1839164). U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, National Quantum Information Science Research Centers, Quantum Science Center.
Brief summary of methods
The group applied a green laser and a microwave onto these spin qubits in a 2D material. The material will then emit photons with different colors (red and near-infrared) under the illumination of a green laser. The rate of photon emission depends on the magnetic field, temperature and pressure. Therefore, the brightness of these spin qubits will change when the magnetic field, temperature or pressure changes. Thus, they were able to accurately measure the magnetic field with high sensitivity.
Writer: Cheryl Pierce
Media contact: Brittany Steff,
Source: Tongcang Li,
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Brittany Steff
Purdue University
Office: 765-494-7833
Cell: 317-439-0771
Expert Contact
Tongcang Li
Purdue University
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








