Home > Press > Optical tweezer technology tweaked to overcome dangers of heat
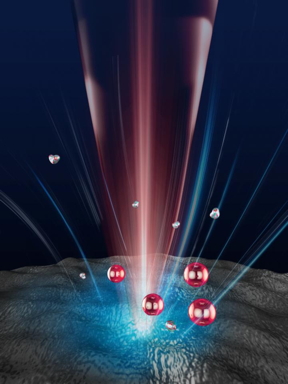 |
| Optical tweezers use light to trap particles for analysis. A new breakthrough keeps those particles from overheating. CREDIT The University of Texas at Austin |
Abstract:
Three years ago, Arthur Ashkin won the Nobel Prize for inventing optical tweezers, which use light in the form of a high-powered laser beam to capture and manipulate particles. Despite being created decades ago, optical tweezers still lead to major breakthroughs and are widely used today to study biological systems.
Optical tweezer technology tweaked to overcome dangers of heat
Austin, TX | Posted on June 25th, 2021However, optical tweezers do have flaws. The prolonged interaction with the laser beam can alter molecules and particles or damage them with excessive heat.
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have created a new version of optical tweezer technology that fixes this problem, a development that could open the already highly regarded tools to new types of research and simplify processes for using them today.
The breakthrough that avoids this problem of overheating comes out of a combination of two concepts: the use of a substrate composed of materials that are cooled when a light is shined on them (in this case, a laser); and a concept called thermophoresis, a phenomenon in which mobile particles will commonly gravitate toward a cooler environment.
The cooler materials attract particles, making them easier to isolate, while also protecting them from overheating. By solving the heat problem, optical tweezers could become more widely used to study biomolecules, DNA, diseases and more.
"Optical tweezers have many advantages, but they are limited because whenever the light captures objects, they heat up," said Yuebing Zheng, the corresponding author of a new paper published in Science Advances and an associate professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering. "Our tool addresses this critical challenge; instead of heating the trapped objects, we have them controlled at a lower temperature."
Optical tweezers do the same thing as regular tweezers -- pick up small objects and manipulate them. However, optical tweezers work at a much smaller scale and use light to capture and move objects.
Analyzing DNA is a common use of optical tweezers. But doing so requires attaching nano-sized glass beads to the particles. Then to move the particles, the laser is shined on the beads, not the particles themselves, because the DNA would be damaged by the heating effect of the light.
"When you are forced to add more steps to the process, you increase uncertainty because now you have introduced something else into the biological system that may impact it," Zheng said.
This new and improved version of optical tweezers eliminates these extra steps.
The team's next steps include developing autonomous control systems, making them easier for people without specialized training to use and extending the tweezers' capabilities to handle biological fluids such as blood and urine. And they are working to commercialize the discovery.
Zheng and his team have much variety in their research, but it all centers on light and how it interacts with materials. Because of this focus on light, he has closely followed, and used, optical tweezers in his research. The researchers were familiar with thermophoresis and hoped they could trigger it with cooler materials, which would actually draw particles to the laser to simplify analysis.
###
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of General Medical Sciences and the National Science Foundation. Other authors are Jingang Li and Zhihan Chen of UT's Texas Materials Institute; Yaoran Liu of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering; Pavana Siddhartha Kollipara of the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering; and Yichao Feng and Zhenglong Zhang of Shaanxi Normal University's School of Physics and Information in China.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nat Levy
@UTAustin
Copyright © University of Texas at Austin
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








