Home > Press > Graphene drum: Researchers develop new phonon laser design
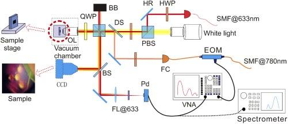 |
| Schematic representation of an experimental setup for receiving and recording phonon radiation. CREDIT Konstantin Arutyunov et al. |
Abstract:
Professor Konstantin Arutyunov of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM HSE), together with Chinese researchers, has developed a graphene-based mechanical resonator, in which coherent emission of sound energy quanta, or phonons, has been induced. Such devices, called phonon lasers, have wide potential for application in information processing, as well as classical and quantum sensing of materials. The study is published in the journal Optics Express.
Graphene drum: Researchers develop new phonon laser design
Moscow, Russia | Posted on June 18th, 2021Using an analogy with photons, quanta of the electromagnetic spectrum, there are also particles of sound energy, phonons. In fact, these are artificially introduced objects in physics - quasi-particles, which correspond to vibrations of the crystal lattice of matter.
Some substances, when irradiated, emit photons of the same wavelength, phase, and polarisation. This process, called stimulated emission, was predicted by Albert Einstein over a century ago and is the basis of the device we all know - the laser. The first lasers were constructed about sixty years ago, and they have become firmly established in our lives in various fields.
A similar process, involving the emission of 'identical' phonons, underlies a device called, by analogy, a phonon laser, or saser. In fact, it was predicted at the same time as lasers, but only a few experimental realisations have been developed over a long period of time, and none of them have been widely used in the industry.
Magnesium ions, semiconductors, composite systems with microcavities, electromechanical resonators, nanoparticles, and many other substances and systems have been used as active media for phonon lasers over the last decade. Unlike previous studies, the present study used graphene to create coherent acoustic excitations. Due to the unique properties of graphene, such resonators can potentially be widely used.
The graphene resonator was produced by microlithography: a photo-sensitive polymer film is deposited on a silicon substrate. Using ultraviolet light, a certain structure is 'drawn' on the substrate, which subsequently allows the formation of a repeating system of micro-cavities by means of plasma treatment. The treated substrate is covered with a layer of graphene, and this system of 'drums' behaves like a resonator, i.e. it amplifies external vibrations if they are generated with a certain frequency.
If such a 'drum' is irradiated with laser light at a specific wavelength, photons are repeatedly reflected between the silicon backing and the graphene, thereby forming optical cavities where mechanical vibrations of the appropriate frequency are produced.
'Experimentally, we have examined a nanostructure, which is a fixed membrane made of a monatomic layer of carbon, or a graphene. Vibrations of atoms, or phonons, were activated in it through exposure to external optical radiation,' says Konstantin Arutyunov. 'The research is expected to continue, as it is of considerable interest both for physics of ultra small objects and has the potential to create a new generation of quantum optomechanical sensors and transducers.'
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liudmila Mezentseva
7-926-313-2406
@HSE_eng
Copyright © National Research University Higher School of Economics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








