Home > Press > Proliferation of electric vehicles based on high-performance, low-cost sodium-ion battery:A large-capacity anode material is developed for sodium-ion batteries by using low-cost silicone-based oil. This process, if commercialized, is expected to significantly reduce manufacturing
 |
| Graphical abstract CREDIT Korea Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) |
Abstract:
Various automobile companies are preparing to shift from internal combustion (IC) engine vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs). However, due to higher cost, EVs are not as easily accessible to consumers; hence, several governments are subsidizing EVs to promote sales. For EV costs to compete with those of IC engine vehicles, their batteries, which account for about 30% of their cost, must be more economical than that of IC-based vehicles.
Proliferation of electric vehicles based on high-performance, low-cost sodium-ion battery:A large-capacity anode material is developed for sodium-ion batteries by using low-cost silicone-based oil. This process, if commercialized, is expected to significantly reduce manufacturing
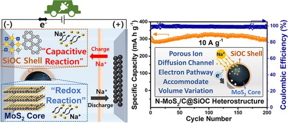
Sejong, Korea | Posted on June 18th, 2021The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has announced that Dr. Sang-Ok Kim's team at the Center for Energy Storage Research had developed a novel, high-performance, economical anode material for use in sodium-ion secondary batteries, which are more cost-effective than lithium-ion batteries. This novel material can store 1.5 times more electricity than the graphite anode used in commercial lithium-ion batteries and its performance does not degrade even after 200 cycles at very fast charging/discharging rates of 10 A/g.
Sodium is over 500 times more abundant in the Earth's crust than lithium; hence, sodium-ion batteries have drawn considerable attention as the next-generation secondary battery because it is 40% cheaper than lithium-ion batteries. However, compared to lithium ions, sodium ions are larger and, thus, cannot be stored as stably in graphite and silicon, which are widely used as anodes in such batteries. Hence, the development of a novel, high-capacity anode material is necessitated.
The KIST research team used molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a metal sulfide that has garnered interest as a candidate for large-capacity anode materials. MoS2 can store a large amount of electricity, but cannot be used because of its high electrical resistance and structural instability that occur during battery operation. However, Dr. Sang-Ok Kim's team overcame this problem by creating a ceramic nano-coating layer using silicone oil, which is a low-cost, eco-friendly material. Through the simple process of mixing the MoS2 *precursor with silicone oil and heat-treating the mixture, they could produce a stable heterostructure with low resistance and enhanced stability.
*precursor : A material in a stage before becoming a specific material in a metabolism or reaction.
**Heterostructure: A structure created by combining two or more materials
Furthermore, the evaluation of electrochemical properties indicated that this material could stably store at least twice as much electricity (?600 mAh/g) as the MoS2 material without coating and could maintain this capacity even after 200 rapid charge/discharge cycles. This excellent performance was achieved by the formation of the ceramic nano-coating layer with high electric storage capacity, which imparts high conductivity and rigidity to the MoS2 surface, resulting in low electrical resistance of the material and high structural stability.
Dr. Sang-Ok Kim, stated "We could successfully solve the high resistance and structural instability problems of MoS2 through the nano-coating surface stabilization technology. As a result, we could develop a sodium-ion battery that can stably store a large amount of electricity. Our method uses cost-effective, eco-friendly materials and, if adapted for the large-scale manufacturing of anode materials, can lower production costs and, hence, boost the commercialization of sodium-ion batteries for large-capacity power storage devices."
###
This study was supported by a KIST's institutional R&D project and the Korea Research Foundation's Outstanding New Researcher Support Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) The results of this study were published in the latest issue of the international journal in nanotechnology 'ACS Nano' (IF: 14.588, top 5.260% in JCR).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Do-Hyun Kim
82-295-86344
Copyright © National Research Council of Science & Technology(NST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








