Home > Press > Changing a 2D material's symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic
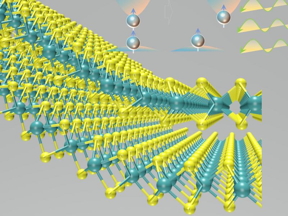 |
| Deforming MoS2 leads to the observation of the flexo-photovoltaic effect. Image credit: Jie Jiang, Jian Shi |
Abstract:
Optoelectronic materials that are capable of converting the energy of light into electricity, and electricity into light, have promising applications as light-emitting, energy-harvesting, and sensing technologies. However, devices made of these materials are often plagued by inefficiency, losing significant useful energy as heat. To break the current limits of efficiency, new principles of light-electricity conversion are needed.
Changing a 2D material's symmetry can unlock its promise: Jian Shi Research Group engineers material into promising optoelectronic
Troy, NY | Posted on June 18th, 2021For instance, many materials that exhibit efficient optoelectronic properties are constrained by inversion symmetry, a physical property that limits engineers' control of electrons in the material and their options for designing novel or efficient devices. In research published today in Nature Nanotechnology, a team of materials scientists and engineers, led by Jian Shi, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used a strain gradient in order to break that inversion symmetry, creating a novel optoelectronic phenomenon in the promising material molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) -- for the first time.
To break the inversion symmetry, the team placed a vanadium oxide (VO2) wire underneath a sheet of MoS2. Molybdenum disulfide is a flexible material, Shi said, so it deformed its original shape to follow the curve of the VO2 wire, creating a gradient within its crystal lattice. Imagine what would happen if you placed a piece of paper over a pencil that was sitting on a table. The varied tension created in the paper is like the strain gradient formed in the MoS2 lattice.
That gradient, Shi said, breaks the material's inversion symmetry and allows electrons traveling within the crystal to be manipulated. The unique photo-response observed near the strain gradient allows a current to flow through the material. It's known as the flexo-photovoltaic effect, and it could be harnessed to design novel and/or high-efficiency optoelectronics.
"This is the first demonstration of such an effect in this material," Shi said. "If we have a solution that does not create heat during photon-electricity conversion, then the electronic devices or circuits could be improved."
Vanadium oxide is very sensitive to temperature, so the team was also able to demonstrate that the flexo-photovoltaic effect brought about temperature dependence at the site where the MoS2 and VO2 materials meet -- changing the lattice's gradient accordingly.
"This discovery suggests a novel principle that could be used for remote thermal sensing," said Jie Jiang, a postdoctoral research fellow in Shi's lab and the first author on this paper.
What the team was able to demonstrate here, Shi said, not only shows great promise for this material, but also suggests the potential of using such an approach in engineering other materials with favorable optoelectronic properties that are plagued by inversion symmetry.
####
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Founded in 1824, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is America's first technological research university. Rensselaer encompasses five schools, 32 research centers, more than 145 academic programs, and a dynamic community made up of more than 7,600 students and over 100,000 living alumni. Rensselaer faculty and alumni include more than 145 National Academy members, six members of the National Inventors Hall of Fame, six National Medal of Technology winners, five National Medal of Science winners, and a Nobel Prize winner in Physics. With nearly 200 years of experience advancing scientific and technological knowledge, Rensselaer remains focused on addressing global challenges with a spirit of ingenuity and collaboration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Torie Wells
518-276-3247
@rpinews
Copyright © Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








