Home > Press > Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties
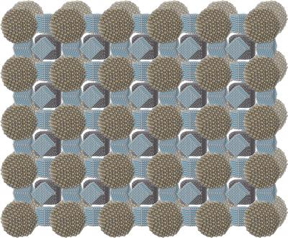 |
| Researchers combined perovskite nanocubes - tiny crystals with useful electrical or optical properties - with spherical nanoparticles to form a regular, repeating structure called a superlattice. Some of these structures displayed superfluorescence, "a burst of photons." CREDIT Image courtesy of Maksym Kovalenko and Ihor Cherniukh/ETH Zürich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology |
Abstract:
Researchers have developed new types of materials that combines two or three types of nanoparticles into structures that display fundamental new properties such as superfluorescence.
Researchers build structured, multi-part nanocrystals with super light-emitting properties
Ames, IA | Posted on May 28th, 2021"The whole goal of this research is to make new materials with new properties and/or exotic new structures," said Alex Travesset, an Iowa State University professor of physics and astronomy and an associate scientist for the U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory. "Those materials are made of very tiny materials, nanoparticles, and lead to properties not shared by more traditional materials made of atoms and molecules."
In this case, an international research team is combining perovskite nanocubes - tiny crystals with useful electrical or optical properties - with spherical nanoparticles to form a regular, repeating structure called a superlattice. The researchers successfully assembled three different superlattices, with one displaying superfluorescence, while another did not.
"This is an example of how structure determines function," Travesset said.
The researchers reported their discovery in a paper just published by the journal Nature that also made the issue's cover.
Maksym Kovalenko, a professor of chemistry and applied biosciences at ETH Zürich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, is the leader of the project and the paper's corresponding author. Ihor Cherniukh, a doctoral student at ETH Zürich, is the first author.
This is the first time such nanoparticles have been combined, the researchers reported in the paper.
Travesset, whose campus website identifies him as a professor of "All things nanoparticles," said he provided the group with theoretical and computational guidance that established what structures would be possible and also made quantitative predictions.
It turned out the predictions were in agreement with the experimental results.
Travesset said the project demonstrates it's "the structure that determines the optoelectronic properties. These are properties that depend on the actual structures - on how the particles are arranged."
A four-year, $385,000 grant from the National Science Foundation supported Travesset's work on the project.
Researchers at ETH Zürich assembled the nanoparticles and researchers at IBM Research Europe measured the nanoparticles' superfluorescent properties.
Although the goal for this project was to advance fundamental science, Travesset said the basic discovery will lead to some practical uses such as ultrabright, quantum light sources.
Perovskite materials are very efficient at turning sunlight into electricity, and so they're being studied for use in solar cells. Now, with the assembly techniques discovered in this project, Travesset said different nanoparticles could be combined to produce novel materials with simultaneous complementary properties.
"We can now take the amazing properties of perovskites," Travesset said, "and combine them with nanoparticles with complementary properties and design materials that perform several functions at the same time."
The Research Team
Iowa State University, Ames Laboratory: Alejandro Travesset
ETH Zürich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology: Maksym Kovalenko, Ihor Cherniukh, Gabriele Rainò, Maryna Bodnarchuk
IBM Research Europe, Zürich: Thilo Stöferle, Rainer Mahrt
Paul Scherrer Institute, Switzerland: Max Burian
Graz University of Technology, Austria: Denys Naumenko, Heinz Amenitsch
Empa, the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Testing and Research: Rolf Erni
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alex Travesset
515-294-7191
@IowaStateUNews
Copyright © Iowa State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Perovskites
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








