Home > Press > Graphene key for novel hardware security
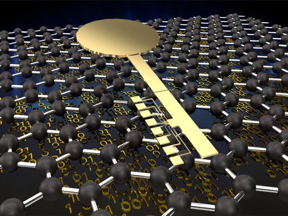 |
| A team of Penn State researchers has developed a new hardware security device that takes advantage of microstructure variations to generate secure keys. CREDIT Jennifer McCann,Penn State |
Abstract:
As more private data is stored and shared digitally, researchers are exploring new ways to protect data against attacks from bad actors. Current silicon technology exploits microscopic differences between computing components to create secure keys, but artificial intelligence (AI) techniques can be used to predict these keys and gain access to data. Now, Penn State researchers have designed a way to make the encrypted keys harder to crack.
Graphene key for novel hardware security
University Park, PA | Posted on May 10th, 2021Led by Saptarshi Das, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics, the researchers used graphene -- a layer of carbon one atom thick -- to develop a novel low-power, scalable, reconfigurable hardware security device with significant resilience to AI attacks. They published their findings in Nature Electronics today (May 10).
"There has been more and more breaching of private data recently," Das said. "We developed a new hardware security device that could eventually be implemented to protect these data across industries and sectors."
The device, called a physically unclonable function (PUF), is the first demonstration of a graphene-based PUF, according to the researchers. The physical and electrical properties of graphene, as well as the fabrication process, make the novel PUF more energy-efficient, scalable, and secure against AI attacks that pose a threat to silicon PUFs.
The team first fabricated nearly 2,000 identical graphene transistors, which switch current on and off in a circuit. Despite their structural similarity, the transistors' electrical conductivity varied due to the inherent randomness arising from the production process. While such variation is typically a drawback for electronic devices, it's a desirable quality for a PUF not shared by silicon-based devices.
After the graphene transistors were implemented into PUFs, the researchers modeled their characteristics to create a simulation of 64 million graphene-based PUFs. To test the PUFs' security, Das and his team used machine learning, a method that allows AI to study a system and find new patterns. The researchers trained the AI with the graphene PUF simulation data, testing to see if the AI could use this training to make predictions about the encrypted data and reveal system insecurities.
"Neural networks are very good at developing a model from a huge amount of data, even if humans are unable to," Das said. "We found that AI could not develop a model, and it was not possible for the encryption process to be learned."
This resistance to machine learning attacks makes the PUF more secure because potential hackers could not use breached data to reverse engineer a device for future exploitation, Das said. Even if the key could be predicted, the graphene PUF could generate a new key through a reconfiguration process requiring no additional hardware or replacement of components.
"Normally, once a system's security has been compromised, it is permanently compromised," said Akhil Dodda, an engineering science and mechanics graduate student conducting research under Das's mentorship. "We developed a scheme where such a compromised system could be reconfigured and used again, adding tamper resistance as another security feature."
With these features, as well as the capacity to operate across a wide range of temperatures, the graphene-based PUF could be used in a variety of applications. Further research can open pathways for its use in flexible and printable electronics, household devices and more.
###
Paper co-authors include Dodda, Shiva Subbulakshmi Radhakrishnan, Thomas Schranghamer and Drew Buzzell from Penn State; and Parijat Sengupta from Purdue University. Das is also affiliated with the Penn State Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Materials Research Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Lakatos
814-865-5544
@penn_state
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Artificial Intelligence
![]() New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
New quantum encoding methods slash circuit complexity in machine learning November 8th, 2024
![]() Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past: New diffusion model approach solves the aspect ratio problem September 13th, 2024
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








