Home > Press > Less innocent than it looks: Hydrogen in hybrid perovskites: Researchers identify the defect that limits solar-cell performance
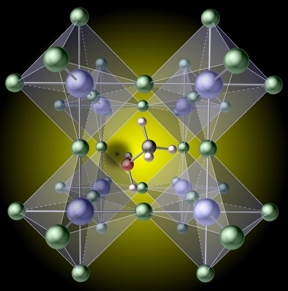 |
| A hydrogen vacancy (the black spot left of center) created by removing hydrogen from a methylammonium molecule, traps carriers in the prototypical hybrid perovskite, mehtylammonium lead iodide CH3NH3Pbl3 CREDIT Xie Zhang |
Abstract:
Researchers in the materials department in UC Santa Barbara's College of Engineering have uncovered a major cause of limitations to efficiency in a new generation of solar cells.
Less innocent than it looks: Hydrogen in hybrid perovskites: Researchers identify the defect that limits solar-cell performance
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on April 30th, 2021Various possible defects in the lattice of what are known as hybrid perovskites had previously been considered as the potential cause of such limitations, but it was assumed that the organic molecules (the components responsible for the "hybrid" moniker) would remain intact. Cutting-edge computations have now revealed that missing hydrogen atoms in these molecules can cause massive efficiency losses. The findings are published in a paper titled "Minimizing hydrogen vacancies to enable highly efficient hybrid perovskites," in the April 29 issue of the journal Nature Materials.
The remarkable photovoltaic performance of hybrid perovskites has created a great deal of excitement, given their potential to advance solar-cell technology. "Hybrid" refers to the embedding of organic molecules in an inorganic perovskite lattice, which has a crystal structure similar to that of the perovskite mineral (calcium titanium oxide). The materials exhibit power-conversion efficiencies rivaling that of silicon, but are much cheaper to produce. Defects in the perovskite crystalline lattice, however, are known to create unwanted energy dissipation in the form of heat, which limits efficiency.
A number of research teams have been studying such defects, among them the group of UCSB materials professor Chris Van de Walle, which recently achieved a breakthrough by discovering a detrimental defect in a place no one had looked before: on the organic molecule.
"Methylammonium lead iodide is the prototypical hybrid perovskite," explained Xie Zhang, lead researcher on the project. "We found that it is surprisingly easy to break one of the bonds and remove a hydrogen atom on the methylammonium molecule. The resulting 'hydrogen vacancy' then acts as a sink for the electric charges that move through the crystal after being generated by light falling on the solar cell. When these charges get caught at the vacancy, they can no longer do useful work, such as charging a battery or powering a motor, hence the loss in efficiency."
The research was enabled by advanced computational techniques developed by the Van de Walle group. Such state-of-the-art calculations provide detailed information about the quantum-mechanical behavior of electrons in the material. Mark Turiansky, a senior graduate student in Van de Walle's group who was involved in the research, helped build sophisticated approaches for turning this information into quantitative values for rates of charge carrier trapping.
"Our group has created powerful methods for determining which processes cause efficiency loss," Turiansky said, "and it is gratifying to see the approach provide such valuable insights for an important class of materials."
"The computations act as a theoretical microscope that allows us to peer into the material with much higher resolution than can be achieved experimentally," Van de Walle explained. "They also form a basis for rational materials design. Through trial and error, it has been found that perovskites in which the methylammonium molecule is replaced by formamidinium exhibit better performance. We are now able to attribute this improvement to the fact that hydrogen defects form less readily in the formamidinium compound.
"This insight provides a clear rationale for the empirically established wisdom that formamidinium is essential for realizing high-efficiency solar cells," he added. "Based on these fundamental insights, the scientists who fabricate the materials can develop strategies to suppress the harmful defects, boosting additional efficiency enhancements in solar cells."
###
Funding for this research was provided by the Department of Energy's Office of Science and Office of Basic Energy Sciences. The computations were performed at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Badham
@ucsantabarbara
Copyright © University of California, Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Perovskites
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








