Home > Press > CEA-Leti Envisions Widespread Use of LiDAR Systems Based on Integrated Optical Phased Arrays (OPAs): OPAs with Solid-State Beam Steering Can Reduce the Cost and Size of LiDAR Systems & Improve Performance; Results Reported at Photonics West 2021
 |
Abstract:
Taking a critical step toward developing LiDAR systems for widespread commercial applications, CEA-Leti has developed genetic algorithms to calibrate high-channel-count optical phased arrays (OPAs), as well as an advanced measurement setup enabling wafer-scale OPA characterization.
CEA-Leti Envisions Widespread Use of LiDAR Systems Based on Integrated Optical Phased Arrays (OPAs): OPAs with Solid-State Beam Steering Can Reduce the Cost and Size of LiDAR Systems & Improve Performance; Results Reported at Photonics West 2021
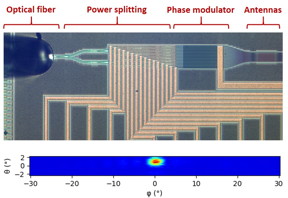
Grenoble, France | Posted on March 9th, 2021OPAs are an emerging technology made of arrays of closely spaced (around 1µm) optical antennas and which radiate coherent light in a broad angular range. The produced interference pattern can then be changed by adjusting the relative phase of the light emitted by each antenna. For example, if the phase gradient between the antennas is linear, a directional beam will be formed. By changing the slope of the linear gradient, the direction of the beam can be controlled, which enables solid-state beam steering.
This can improve performance in scanning speed, power efficiency and resolution compared to the heavy, power-hungry and expensive mechanical beam-steering systems used in current LiDARs. An additional feature of OPA-based LiDAR systems is that they have no moving parts, as the solid-state beam steering is achieved only by phase tuning the antennas, which significantly reduces the size and cost of these systems.
CEA-Leti reported the calibration and characterization results at Photonics West 2021 Digital Forum, in a paper titled “Development, Calibration and Characterization of Silicon Photonics-Based Optical Phased Arrays”.
“The development of a high-performance OPA would pave the way to inexpensive LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, holographic displays, biomedical imaging and many other applications,” said Sylvain Guerber, the lead author of the paper. “But widespread adoption of LiDAR will hinge on lower system costs and smaller form factors.”
LiDAR, which stands for light detection and ranging, has emerged as a key enabling technology for tomorrow’s sensing and vision systems. In addition to automotive and medical uses, they could enable autonomous mobility for drones and robots, as well as industrial automation. Commercial LiDAR systems must meet stringent requirements, especially for automotive applications. In particular, a high-power and low-divergence beam is needed to accurately resolve a scene. For example, resolving a 10cm object at 100m requires an OPA operating at a wavelength of 1µm with a circuit consisting of at least 1,000 antennas, each spaced 1µm apart. Therefore, the development of high-channel-count OPAs is necessary for a commercial OPA-based LiDAR system.
An integrated chip-scale OPA with solid-state beam steering can be produced by leveraging the benefits of a mature silicon photonics platform, Guerber said. However, this is only the first step toward a fully functional OPA because beam scanning requires a preliminary calibration. Due to the high number of required optical antennas, this calibration process can take a large amount of time, which is incompatible with massive deployment of a technology. Thus, the CEA-Leti team has developed what may be the first wafer-scale OPA characterization setup, which is an important step toward industrialization of OPA-based LiDARs. In addition, genetic algorithms based on Darwin’s theory of evolution have been developed to quickly and reliably calibrate high-channel-count OPAs. These allow up to 1,000x faster calibration than previously used algorithms.
Guerber noted that broad commercial adoption of LiDAR technology by the automotive industry and other markets is projected to be several years down the road. OPAs are a critical step, which CEA-Leti will continue to work on.
“There are still a lot of challenges, especially at the system level,” he explained. “A LiDAR is composed of many elements: a laser, an electronic driver, an OPA steering system, a detector and data-treatment capability. All of them must work together; the OPA is only a part of the system.”
This work was partially funded by the French ANR via Carnot funding, the ECSEL Vizta European project and the French National Program “Programme d’investissement d’avenir, IRT Nanoelec, n° ANR-10-AIRT-05
####
About CEA Leti
CEA-Leti, a technology research institute at CEA, is a global leader in miniaturization technologies enabling smart, energy-efficient and secure solutions for industry. Founded in 1967, CEA-Leti pioneers micro- & nanotechnologies, tailoring differentiating applicative solutions for global companies, SMEs and startups. CEA-Leti tackles critical challenges in healthcare, energy and digital migration. From sensors to data processing and computing solutions, CEA-Leti’s multidisciplinary teams deliver solid expertise, leveraging world-class pre-industrialization facilities. With a staff of more than 1,900, a portfolio of 3,100 patents, 12,000 sq. meters of cleanroom space and a clear IP policy, the institute is based in Grenoble, France, and has offices in Silicon Valley and Tokyo. CEA-Leti has launched 69 startups and is a member of the Carnot Institutes network. Follow us on www.leti-cea.com and @CEA_Leti.
Technological expertise
CEA has a key role in transferring scientific knowledge and innovation from research to industry. This high-level technological research is carried out in particular in electronic and integrated systems, from microscale to nanoscale. It has a wide range of industrial applications in the fields of transport, health, safety and telecommunications, contributing to the creation of high-quality and competitive products.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Press Contact
Agency
+33 6 74 93 23 47
Copyright © CEA Leti
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








