Home > Press > Dynamic 3D printing process features a light-driven twist: Light provides freedom to control each layer and improves precision and speed
 |
Abstract:
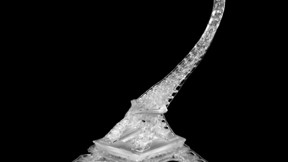
•Demos include a customized vascular stent, double helix and contorted Eiffel Tower printed on the fly
•‘We are using light to do the manufacturing,’ researcher says
•Flexible robotic arm and photopolymer also key in process
•Four thousand layers can be printed in about two minutes
Dynamic 3D printing process features a light-driven twist: Light provides freedom to control each layer and improves precision and speed
Evanston, IL | Posted on February 4th, 2021The speed of light has come to 3D printing. Northwestern University engineers have developed a new method that uses light to improve 3D printing speed and precision while also, in combination with a high-precision robot arm, providing the freedom to move, rotate or dilate each layer as the structure is being built.
Most conventional 3D printing processes rely on replicating a digital design model that is sliced into layers with the layers printed and assembled upwards like a cake. The Northwestern method introduces the ability to manipulate the original design layer by layer and pivot the printing direction without recreating the model. This “on-the-fly” feature enables the printing of more complicated structures and significantly improves manufacturing flexibility.
“The 3D printing process is no longer a way to merely make a replica of the designed model,” said Cheng Sun, associate professor of mechanical engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering. “Now we have a dynamic process that uses light to assemble all the layers but with a high degree of freedom to move each layer along the way.”
Sun led the research, which lies at the intersection of two of his main areas of focus: nanofabrication and optics. The study was published today (Feb. 3) by the journal Advanced Materials.
In the paper, the researchers demonstrate several applications, including 3D printing a customized vascular stent and printing a soft pneumatic gripper made of two different materials, one hard and one soft. A double helix and a tiny Eiffel Tower are two other printed examples in the study.
The Northwestern process uses a robotic arm and a liquid photopolymer that is activated by light. Sophisticated 3D structures are pulled out from a bath of liquid resin by a high-precision robot with enhanced geometric complexity, efficiency and quality compared to the traditional printing process. The arm is used to change the printing direction dynamically.
“We are using light to do the manufacturing,” Sun said. “Shining light on the liquid polymer causes it to crosslink, or polymerize, converting the liquid to a solid. This contributes to the speed and precision of our 3D printing process -- two major challenges that conventional 3D printing is facing.”
The continuous printing process can print 4,000 layers in approximately two minutes.
“This is a very fast process, and there is no interruption between layers,” Sun said. “We hope the manufacturing industry will find benefit in it. The general printing method is compatible with a wide range of materials.”
Looking to the future, Sun said this printing process could be applied to other additive as well as traditional subtractive manufacturing processes, providing a bridge toward a truly hybrid process.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant R01HL141933) and the National Science Foundation (grant EEC‐1530734).
The title of the paper is “Conformal Geometry and Multimaterial Additive Manufacturing through Freeform Transformation of Building Layers.”
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Megan Fellman
(847) 491-3115
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Robotics
![]() Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
Nanofibrous metal oxide semiconductor for sensory face November 8th, 2024
![]() Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
Femtosecond laser technique births "dancing microrobots": USTC's breakthrough in multi-material microfabrication August 11th, 2023
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








