Home > Press > High-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution: The group has realized a scanless 3D imaging system and an algorithm for high-speed measurement
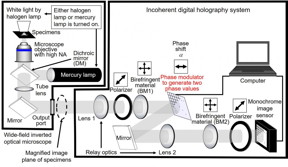 |
| Overview of the developed high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system for scanless 3D measurement with submicron resolution. CREDIT National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Tohoku University, Toin University of Yokohama, Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) |
Abstract:
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Tohoku University, Toin University of Yokohama, and Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) have succeeded in developing a scanless high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution for a 3D space. The system is based on digital holography. The developed microscopy system has an algorithm to acquire 3D information of fluorescent objects toward scanless 3D measurement in less than 1 millisecond. Scanless 3D sensing with submicron resolution and color-multiplexed holographic fluorescence imaging have been demonstrated using the algorithm. The microscopy system will be further developed to achieve holographic 3D motion-picture sensing of specimens with incoherent light.
This achievement was published in Optics Letters as an open-access paper on January 29, 2021.
High-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system with submicron resolution: The group has realized a scanless 3D imaging system and an algorithm for high-speed measurement
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on January 29th, 2021[Achievements]
The scanless high-speed holographic fluorescence microscopy system shown in Figure 1 was constructed. The system is based on digital holography and is applicable to the sensing of incoherent light such as fluorescence light and natural light. The developed algorithm enables the adoption of a phase modulator to generate two phase values, which is expected to increase the measurement speed. Submicron resolution for a 3D space was successfully demonstrated using fluorescent objects with a diameter of 0.2 micron. The experimental results shown in Figure 2 indicate that the developed microscopy system achieves 3D sensing of nanoparticles and has submicron resolution quantitatively for a 3D space. Scanless 3D measurement in less than 1 millisecond is achievable by using the algorithm with either a ferroelectric liquid crystal on silicon (FLCOS) or an electro-optic (EO) device. Color-multiplexed holographic fluorescence imaging with the algorithm and only four exposures has also been demonstrated by combining the proposed algorithm and computational coherent superposition (CCS). The number of exposures is reduced by the algorithm, and the number of photons per hologram is increased even for ultimately weak light.
[Future prospects]
High-speed holographic motion-picture imaging for 3D dynamics and multiple moving objects in a 3D space.
Improvements of the system such as recording of a quantitative phase, sensing of ultimately weak light, and construction of a compact optical setup.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
HIROTA Sachiko
Copyright © National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








