Home > Press > Islands without structure inside metal alloys could lead to tougher materials: These high-entropy alloys could lead to better technologies in transportation, energy and denfense
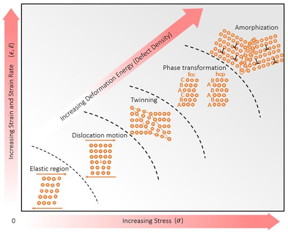 |
| Proposed hierarchical deformation mechanism paradigm for the equi- atomic CrCoNi-based HEAs subjected to increasing degrees of deformation. Elastic deformation, dislocation-mediated plasticity, twinning-induced plasticity, TRIP, and finally solid-state amorphization. Triggering the next mechanism re- quires the generation of additional defects, i.e., dislocations and/or point defects (vacancies). These multiple mechanisms can interact, leading to a synergy of strengthening processes and a resulting highly complex microstructure. CREDIT University of California San Diego |
Abstract:
An international team of researchers produced islands of amorphous, non-crystalline material inside a class of new metal alloys known as high-entropy alloys.
Islands without structure inside metal alloys could lead to tougher materials: These high-entropy alloys could lead to better technologies in transportation, energy and denfense
San Diego, CA | Posted on January 29th, 2021This discovery opens the door to applications in everything from landing gears, to pipelines, to automobiles. The new materials could make these lighter, safer, and more energy efficient.
The team, which includes researchers from the University of California San Diego and Berkeley, as well as Carnegie Mellon University and University of Oxford, details their findings in the Jan. 29 issue of Science Advances.
"These present a bright potential for increased strength and toughness since metallic glasses (amorphous metals) have a strength that is vastly superior to that of crystalline metals and alloys," said Marc Meyers, a professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at UC San Diego, and the paper' s corresponding author.
Using transmission electron microscopy, which can identify the arrangement of atoms, the researchers concluded that this amorphization is triggered by extreme deformation at high velocities. It is a new deformation mechanism that can increase the strength and toughness of these high entropy alloys even further.
The research is based on seminal work by Brian Cantor at the University of Oxford, and Jien-Wei Yeh at National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan. In 2004, both researchers led teams that reported the discovery of high-entropy alloys. This triggered a global search for new materials in the same class, driven by numerous potential applications in the transportation, energy, and defense industries.
"Significant new developments and discoveries in metal alloys are quite rare," Meyers said.
###
Amorphization in extreme deformation of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
Shiteng Zhao and Robert O. Ritchie, University of California Berkeley; Zezhou Li, Wen Yang and Marc A. Meyers, University of California San Diego; Chaoyi Zhu, Carnegie Mellon University; Zhouran Zhang, David E. J. Armstrong and Patrick S. Grant, University of Oxford.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ioana Patringenaru
619-253-4474
@UCSanDiego
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
The National Space Society Congratulates SpaceX on Starship’s 7th Test Flight: Latest Test of the Megarocket Hoped to Demonstrate a Number of New Technologies and Systems January 17th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








