Home > Press > Theory describes quantum phenomenon in nanomaterials: Osaka City University scientists have developed mathematical formulas to describe the current and fluctuations of strongly correlated electrons in quantum dots. Their theoretical predictions could soon be tested experimentally
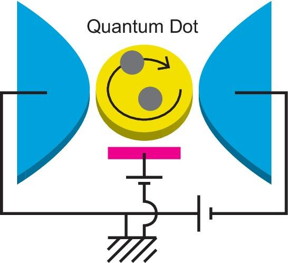 |
| A quantum dot (the yellow part) is connected to two lead electrodes (the blue parts). Electrons tunneling into the quantum dot from the electrodes interact with each other to form a highly correlated quantum state, called "Fermi liquid." Both nonlinear electric current passing through the quantum dot and its fluctuations that appear as a noise carry important signals, which can unveil underlying physics of the quantum liquid. It is clarified that three-body correlations of the electrons evolve significantly and play essential roles in the quantum state under the external fields that break the particle-hole or time-reversal symmetry. CREDIT Rui Sakano |
Abstract:
Theoretical physicists Yoshimichi Teratani and Akira Oguri of Osaka City University, and Rui Sakano of the University of Tokyo have developed mathematical formulas that describe a physical phenomenon happening within quantum dots and other nanosized materials. The formulas, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, could be applied to further theoretical research about the physics of quantum dots, ultra-cold atomic gasses, and quarks.
Theory describes quantum phenomenon in nanomaterials: Osaka City University scientists have developed mathematical formulas to describe the current and fluctuations of strongly correlated electrons in quantum dots. Their theoretical predictions could soon be tested experimentally
Osaka, Japan | Posted on December 25th, 2020At issue is 'the Kondo effect'. This effect was first described in 1964 by Japanese theoretical physicist Jun Kondo in some magnetic materials, but now appears to happen in many other systems, including quantum dots and other nanoscale materials.
Normally, electrical resistance drops in metals as the temperature drops. But in metals containing magnetic impurities, this only happens down to a critical temperature, beyond which resistance rises with dropping temperatures.
Scientists were eventually able to show that, at very low temperatures near absolute zero, electron spins become entangled with the magnetic impurities, forming a cloud that screens their magnetism. The cloud's shape changes with further temperature drops, leading to a rise in resistance. This same effect happens when other external 'perturbations', such as a voltage or magnetic field, are applied to the metal.
Teratani, Sakano and Oguri wanted to develop mathematical formulas to describe the evolution of this cloud in quantum dots and other nanoscale materials, which is not an easy task.
To describe such a complex quantum system, they started with a system at absolute zero where a well-established theoretical model, namely Fermi liquid theory, for interacting electrons is applicable. They then added a 'correction' that describes another aspect of the system against external perturbations. Using this technique, they wrote formulas describing electrical current and its fluctuation through quantum dots.
Their formulas indicate electrons interact within these systems in two different ways that contribute to the Kondo effect. First, two electrons collide with each other, forming well-defined quasiparticles that propagate within the Kondo cloud. More significantly, an interaction called a three-body contribution occurs. This is when two electrons combine in the presence of a third electron, causing an energy shift of quasiparticles.
"The formulas' predictions could soon be investigated experimentally", Oguri says. "Studies along the lines of this research have only just begun," he adds.
The formulas could also be extended to understand other quantum phenomena, such as quantum particle movement through quantum dots connected to superconductors. Quantum dots could be a key for realizing quantum information technologies, such as quantum computers and quantum communication.
####
About Osaka City University
We are Osaka City University - the oldest research university in Osaka. With 9 undergraduate faculties and 11 graduate schools all dedicated to making urban life better, energy cleaner, and people healthier and happier, we have won numerous awards and have produced 2 Nobel laureates. For more information, please visit our website at https://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/en
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Gracey
066-605-3454
@OCU_PR
Copyright © Osaka City University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Superconductivity
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








