Home > Press > A new candidate material for quantum spin liquids
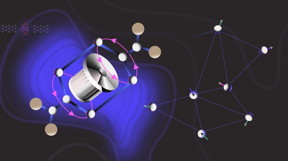 |
| Quantum Spin Liquid driven by molecular rotors. CREDIT Péter Szirmai |
Abstract:
In 1973, physicist and later Nobel laureate Philip W. Anderson proposed a bizarre state of matter: the quantum spin liquid (QSL). Unlike the everyday liquids we know, the QSL actually has to do with magnetism - and magnetism has to do with spin.
A new candidate material for quantum spin liquids
Lausanne, Switzerland | Posted on November 12th, 2020Disordered electron spin produces QSLs
What makes a magnet? It was a long-lasting mystery, but today we finally know that magnetism arises from a peculiar property of sub-atomic particles, like electrons. That property is called "spin", and the best - yet grossly insufficient - way to think of it is like a child's spinning-top toy.
What is important for magnetism is that spin turns every one of a material's billions of electrons into a tiny magnet with its own magnetic "direction" (think north and south pole of a magnet). But the electron spins aren't isolated; they interact with each other in different ways until they stabilize to form various magnetic states, thereby granting the material they belong to magnetic properties.
In a conventional magnet, the interacting spins stabilize, and the magnetic directions of each electron align. This results in a stable formation.
But in what is known as a "frustrated" magnet, the electron spins can't stabilize in the same direction. Instead, they constantly fluctuate like a liquid - hence the name "quantum spin liquid."
Quantum Spin Liquids in future technologies
What is exciting about QSLs is that they can be used in a number of applications. Because they come in different varieties with different properties, QSLs can be used in quantum computing, telecommunications, superconductors, spintronics (a variation of electronics that uses electron spin instead of current), and a host of other quantum-based technologies.
But before exploiting them, we first have to gain a solid understanding of QSL states. To do this, scientists have to find ways to produce QSLs on demand - a task that has proven difficult so far, with only a few materials on offer as QSL candidates.
A complex material might solve a complex problem
Publishing in PNAS, scientists led by Péter Szirmai and Bálint Náfrádi at László Forró's lab at EPFL's School of Basic Sciences have successfully produced and studied a QSL in a highly original material known as EDT-BCO. The system was designed and synthesized by the group of Patrick Batail at Université d'Angers (CNRS).
The structure of EDT-BCO is what makes it possible to create a QSL. The electron spins in the EDT-BCO form triangularly organized dimers, each of which has a spin-1/2 magnetic moment which means that the electron must fully rotate twice to return to its initial configuration. The layers of spin-1/2 dimers are separated by a sublattice of carboxylate anions centred by a chiral bicyclooctane. The anions are called "rotors" because they have conformational and rotational degrees of freedom.
The unique rotor component in a magnetic system makes the material special amongst QSL candidates, representing a new material family. "The subtle disorder provoked by the rotor components introduces a new handle upon the spin system," says Szirmai.
The scientists and their collaborators employed an arsenal of methods to explore the EDT-BCO as a QSL material candidate: density functional theory calculations, high-frequency electron spin resonance measurements (a trademark of Forró's lab), nuclear magnetic resonance, and muon spin spectroscopy. All of these techniques explore the magnetic properties of EDT-BCO from different angles.
All the techniques confirmed the absence of long-range magnetic order and the emergence of a QSL. In short, EDT-BCO officially joins the limited ranks of QSL materials and takes us a step further into the next generation of technologies. As Bálint Náfrádi puts it: "Beyond the superb demonstration of the QSL state, our work is highly relevant, because it provides a tool to obtain additional QSL materials via custom-designed functional rotor molecules."
###
Other contributors
CNRS and Université d'Angers
Czech Academy of Sciences
CNRS and Université de Paris-Sud
Goethe-Universitat Frankfurt
Science and Technology Facilities Council (ISIS Muon Group)
Paul Scherrer Institute
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nik Papageorgiou
41-216-932-105
@EPFL_en
Copyright © Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Quantum chemistry
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








