Home > Press > Spin clean-up method brings practical quantum computers closer to reality: Osaka City University develops a quantum algorithm that removes pesky spin contaminants from chemical calculations on quantum computers
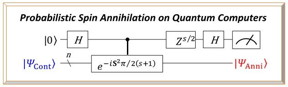 |
| If the measurement outcome in the quantum circuit is the |0? state, the spin contaminated wave function |?Cont? is projected out onto the spin annihilated one |?Anni?. The rightmost part of the top line denotes the measurement. CREDIT Kenji Sugisaki, Kazunobu Sato and Takeji Takui, Osaka City University |
Abstract:
Quantum computers are the new frontier in advanced research technology, with potential applications such as performing critical calculations, protecting financial assets, or predicting molecular behavior in pharmaceuticals. Researchers from Osaka City University have now solved a major problem hindering large-scale quantum computers from practical use: precise and accurate predictions of atomic and molecular behavior.
Spin clean-up method brings practical quantum computers closer to reality: Osaka City University develops a quantum algorithm that removes pesky spin contaminants from chemical calculations on quantum computers
Osaka, Japan | Posted on September 25th, 2020They published their method to remove extraneous information from quantum chemical calculations on Sept. 17 as an advanced online article in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
"One of the most anticipated applications of quantum computers is electronic structure simulations of atoms and molecules," said paper authors Kenji Sugisaki, Lecturer and Takeji Takui, Professor Emeritus in the Department of Chemistry and Molecular Materials Science in Osaka City University's Graduate School of Science.
Quantum chemical calculations are ubiquitous across scientific disciplines, including pharmaceutical therapy development and materials research. All of the calculations are based on solving physicist Erwin Schrödinger's equation, which uses electronic and molecular interactions that result in a particular property to describe the state of a quantum-mechanical system.
"Schrödinger equations govern any behavior of electrons in molecules, including all chemical properties of molecules and materials, including chemical reactions," Sugisaki and Takui said.
On classical computers, such precise equations would take exponential time. On quantum computers, this precision is possible in realistic time, but it requires "cleaning" during the calculations to obtain the true nature of the system, according to them.
A quantum system at a specific moment in time, known as a wave function, has a property described as spin, which is the total of the spin of each electron in the system. Due to hardware faults or mathematical errors, there may be incorrect spins informing the system's spin calculation. To remove these 'spin contaminants,' the researchers implemented an algorithm that allows them to select the desired spin quantum number. This purifies the spin, removing contaminants during each calculation--a first on quantum computers, according to them.
"Quantum chemical calculations based on exactly solving Schrödinger equations for any behavior of atoms and molecules can afford predictions of their physical-chemical properties and complete interpretations on chemical reactions and processes," they said, noting that this is not possible with currently available classical computers and algorithms. "The present paper has given a solution by implementing a quantum algorithm on quantum computers."
The researchers next plan to develop and implement algorithms designed to determine the state of electrons in molecules with the same accuracy for both excited- or ground-state electrons.
###
Other contributors include Kazuo Toyota, Kazunobu Sato and Daisuke Shiomi, all of whom are affiliated with the Department of Chemistry and Molecular Materials Science in Osaka City University's Graduate School of Science. Sugisaki is also affiliated with the Japan Science and Technology Agency's PRESTO Project, "Quantum Software." Takui is also a University Research Administrator in the Research Support Department/University Research Administrator Center of Osaka City University.
####
About Osaka City University
We are Osaka City University - the oldest research university in Osaka. With 9 undergraduate faculties and 11 graduate schools all dedicated to making urban life better, energy cleaner, and people healthier and happier, we have won numerous awards and have produced 2 Nobel laureates. For more information, please visit our website at https://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/en
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Gracey
81-666-053-454
@OCU_PR
Copyright © Osaka City University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








