Home > Press > UTEP researchers help bring biofriendly materials to drug design for neuro disorders
 |
| The contributions of researchers from The University of Texas at El Paso have yielded the first indication that carbon quantum dots, a class of nanoparticles, can be utilized to combat neurological disorders. CREDIT Mahesh Narayan |
Abstract:
The contributions of researchers from The University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP) have yielded the first indication that carbon quantum dots, a class of nanoparticles, can be utilized to combat neurological disorders, according to a paper published in the journal Processes as part its special issue on protein biosynthesis and drug design and delivery.
UTEP researchers help bring biofriendly materials to drug design for neuro disorders
El Paso, TX | Posted on June 5th, 2020The study, titled "Untangling the Potential of Carbon Quantum Dots in Neurodegenerative Disease," was co-authored by Sreeprasad T. Sreenivasan, Ph.D., and Mahesh Narayan, Ph.D., assistant professor and professor, respectively, in UTEP's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry. The pair contributed to work by Prakash Narayan, Ph.D., vice president of preclinical research for Angion Biomedica Corp. in Uniondale, New York; and Lindsey Jung, a student at Tenafly High School in New Jersey, who works under Prakash Narayan's supervision.
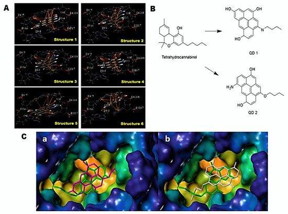
The study focuses on carbon quantum dots (CQDs), biofriendly materials synthesized from waste materials such as wood, fruit peel, algae and even salmon. A road map laid out by the research team addresses, for the first time, key requirements for the transitioning of their use from environmental-sensing applications into the neurodegenerative domain; a crossing-over that requires their separation and total characterization, including aspects related to safety and their ability to target specific receptors in the brain.
"The carbonaceous quanta are finally making their way from physics into chemistry and now, biology," Prakash Narayan said. "This work lays the foundation for harnessing the enormous potential of carbon quantum dots for therapeutic intervention in neuro disease."
The CQDs are made by "pressure-cooking" waste biomaterials such as fruit peel, amino acids, algae and even fish. As an outcome of the procedure, they are synthesized as a mixture of carbon dots and non-carbon dots. Some of the compounds in the mixture can be toxic. This aspect would negate their use in biomedical applications.
To facilitate the crossing-over of CQDs into preclinical and eventually clinical use, the research team provides a path for their safe use while demonstrating their potential to both prevent and treat neurodegenerative disorders, Mahesh Narayan said.
The research was conducted at Angion Biomedica, and at UTEP's Functional Quantum Materials Laboratory and the Laboratory for Neurodegenerative Research.
The transitioning of CQD applications from electrochemistry, catalysis and environmental sensing to biomedicine represents an important milestone in its 15-year history; a bellwether for its yet-unrealized potential in interventional biology, imaging, diagnostics, prophylaxis and therapy.
"This will allow pharmaceutical companies to tailor carbon quantum dots for specific uses," Mahesh Narayan said. "Individuals with Parkinson's and Alzheimer's could benefit greatly from this kind of therapy."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Victor H. Arreola
915-747-6437
@UTEP_Research
Copyright © University of Texas at El Paso
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() To read the full paper, visit:
To read the full paper, visit:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navyís quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








