Home > Press > 2D sandwich sees molecules with clarity: Rice University engineers adapt 2D ‘sandwich’ for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
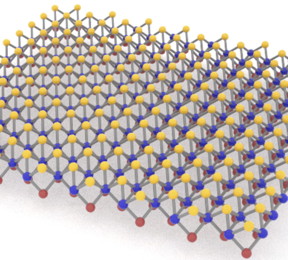 |
| Monolayer Janus MoSSe, a compound of molybdenum, sulfur and selenium developed at Rice University, is adept at detecting biomolecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Its nonmetallic nature helps by curtailing background noise in the signal. (Credit: Lou Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
A sandwich of molybdenum, sulfur and selenium turns out to be deliciously useful for detecting biomolecules.
2D sandwich sees molecules with clarity: Rice University engineers adapt 2D ‘sandwich’ for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Houston, TX | Posted on May 15th, 2020platform for improving the detection of biomolecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).
Using glucose to test the material proved its ability to boost its Raman enhancement factor by more than 100,000 times, which the researchers say is comparable to the highest-reported enhancement factor for 2D substrates.
SERS is an established technique that enables the detection and identification of small concentrations of molecules — or even single molecules — that get close to or adsorbed by metallic surfaces, including nanoparticles. It’s often used to detect nanoscale proteins in bodily fluids, helping to detect diseases and determine treatments, and in environmental analysis.
But metallic SERS media often prompt side reactions that create background noise. Janus MoSSe synthesized at Rice is nonmetallic. “This work mainly addresses whether we can enhance the target molecules' signal strength,” said materials scientist and principal investigator Jun Lou. “We wanted to know if we could make it stand out from the background noise.”
The answer was clearly yes, as Lou and his team reported in Nanoscale.
MoSSe introduced by the Lou lab in 2017 was produced by chemical vapor deposition. Molybdenum sits in the middle with a layer of sulfur on one side and another of selenium on the other; hence the two-faced Janus characterization.
The different electronegativities of each layer make it a SERS superstar, said lead author and Rice alumnus Shuai Jia, a former graduate student in Lou’s lab.
“The dipole created between the top sulfur and the bottom selenium lands out-of-plane, and this creates an electrical field a few nanometers beyond the MoSSe,” Jia said. That field interacts with molecules that come close, enhancing their vibrational intensity enough to be detected.
The researchers noted tests with MoSSe also detected molecules of the neurotransmitter dopamine and that the substrate should be adaptable to sense other molecules.
Lou said there’s room for improvement. “We’re looking at hybrids of MoSSe with some metallic nanoparticles, and also trying to enhance the dipole strength,” he said.
Co-authors of the paper are postdoctoral researchers Jing Zhang and Weipeng Wang and graduate student Tianshu Zhai of Rice, and postdoctoral researchers Arkamita Bandyopadhyay and Hemant Kumar and Vivek Shenoy, the Eduardo D. Glandt President's Distinguished Professor of materials science and engineering, mechanical engineering and applied mechanics and of bioengineering, at the University of Pennsylvania. Lou is a professor of materials science and nanoengineering and of chemistry.
The Welch Foundation and the National Science Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,962 undergraduates and 3,027 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() 2-faced 2D material is a first at Rice:
2-faced 2D material is a first at Rice:
![]() Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








